Context:
At the United Nations Security Council, India has reiterated its strong support for the just Palestinian cause and its unwavering commitment to the two-state solution.
Background:
- There is an ongoing fight in Israel and the Gaza Strip. Roughly 200 Palestinians have died, and officials say nearly half of them are women and children. Israel has reported at least 10 dead.
- An escalation of fighting between Israelis and Palestinians has led the UN to warn of a “full-scale war”.
History of Jews
- Jews have been persecuted throughout history due to their religious beliefs and foreign culture.
- In 1897, Jews started a movement called a Zionist movement, to escape persecution and establish their own state in their ancestral homeland, Israel. The World Zionist Organisation was created to advocate for the establishment of a Jewish homeland in Palestine.
- As a result, a large number of Jews started flowing into Palestine and they bought land and started settling down there.
- By 1916, Palestine came under British control after the Sykes-Picot Agreement (a secret agreement between Great Britain and France). This led to the divisionof Ottoman Turkish Empire.
- Later through the Balfour Declaration, the British foreign secretary James Balfour agreed to the establishment of a Jewish homeland.
- After the Nazis gained power in Germany in 1930s, the Jews influx to Palestine took a major turn with hundreds of thousands of them resettled from Europe to Palestine. Arabs saw this as a threat to their homeland and they fought bitterly with them. As the British Government remained as a mute spectator, violence reached its peak.
- In 1947, the British Government referred the question of the future of Palestine to the United Nations. UN voted to split the land into two countries. Jewish people accepted the agreement and declared the independence of Israel.

Arab’s fight against the Israel (1948-49)
- Arabs saw the creation of Israel as a part of a conspiracy to move them out of their land. Consequently, in 1948, the Arab states of Egypt, Jordan, Iraq, and Syria declared war on Israel.
- Note: It’s interesting to note here that India opposed the UN resolution and Gandhi called it as a crime against humanity. But India recognized Israel as a country.
- At the end of the war between Israel and Arab countries, Israel emerged victoriously. Moreover, it could increase its territory to a larger extent and it marked the beginning of the expansionist policy of Israel.
- As a consequence of the war, a large number of Palestinians either flee or were forced to move out of Israel and settle in refugee camps near Israel’s border. It was the beginning of Palestine refugee crisis which ultimately led to the creation of a terrorist organization PLO (Palestine Liberation Organization) in 1964.

Israel’s fight against the Arab countries (1967)
In 1967, Israel launched a preemptive strike against Egypt, Syria, and Jordan and at the end of this Six-Day War, Israel captured:
- Golan Heights from Syria.
- West Bank and East Jerusalem from Jordan.
- Sinai Peninsula and Gaza Strip from Egypt. (Refer to the map above)
- The 1967 war is particularly important for today’s conflict, as it left Israel in control of the West Bank and Gaza Strip, two territories home to a large number of Palestinians.
- Gaza and Westbank are together known as ‘Occupied Territories’, after the 1967 war.

UN Charter and return of the Sinai Peninsula
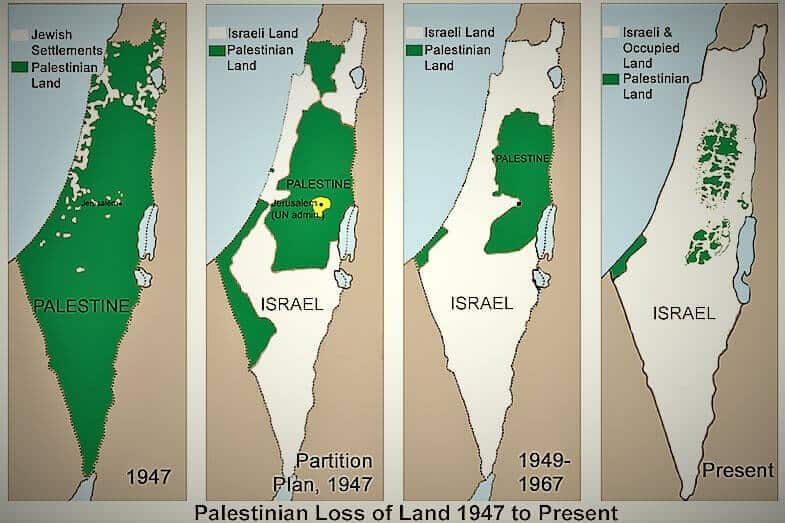
- Under the UN Charter, there can lawfully be no territorial gains from war, even by a state acting in self-defence.
- Therefore, in response to the Six-Day War, the UN Security Council adopted a resolution for ‘Land for peace’ and it mandated that Israel should return the captured areas back to the defeated nations.
- In the light of Israel’s reluctance to return the captured territories, another Arab-Israeli war erupted in 1973 (Yom Kippur war) in which Israel suffered some setbacks.
- In 1979, Israel-Egypt signed a peace treaty, accordingly Israel return the Sinai Peninsula to Egypt (1982). Egypt became the first Arab nation to officially recognize Israel as a state.
- In 1982, Israel invaded Lebanon and ejected the Palestinian Liberation Organisation (PLO).The PLO was formed in 1964 to fight for the “liberation of Palestine” through armed struggle.
- Meanwhile, Israel was creating Jewish settlements in areas that were considered Palestinian territory including in East Jerusalem.
First Palestinian Intifada
- In 1987, there was an uprising of Palestinians against the Israeli occupation of Gaza and the West Bank.
- Hundreds of people were killed and this is called the First Palestinian Intifada (Arabic word meaning ‘shaking off’).
- The Intifada came to an end with the Oslo Peace Accords signed in 1993 and a second accord signed in 1995 between the then Israeli Prime Minister Yitzhak Rabin and Yasser Arafat, the leader of the PLO.
- After this, the Palestinian Authority formed and took control over some territories in Israel.
Second Palestinian Intifada
- The Israeli army withdrew from parts of the West Bank in 1997. However, the Accords could not bring permanent peace to the region and the Second Palestinian Intifada was launched in 2000.
- The trigger of the violence was a visit to the Al Aqsa Mosque in Jerusalem by Israeli politician Ariel Sharon.
- There was widespread rioting and violence which lasted for years.
- A ceasefire was finally announced and Israel planned to withdraw all troops and Jewish settlements from the Gaza Strip by 2005 end.
Second Lebanon War
- This conflict started in July 2006 between Israel and Hezbollah in Lebanon, Golan Heights and Northern Israel.
- It ended after a couple of months through a UN-brokered ceasefire.
- Hezbollah is a Lebanese Shia Islamist political party and militant goup.
Hamas Wars
- Hamas, a Sunni Islamist militant group won the elections in Palestine in 2006.
- In 2007, Hamas defeated Fatah (political group that controlled the PLO) in 2007 in fighting that started in 2006.
- Hamas (which many consider a terrorist group) has been fighting with Israel with particularly significant battles in 2008, 2012 and 2014.
Current Situation
- Hamas rules over Gaza.
- Gaza’s borders are tightly controlled by Israel and Egypt.
- The West Bank is still occupied by Israel.
- Most Palestinian refugees and their descendants live in Gaza, the West Bank, East Jordan, Syria and Lebanon.
- Tensions run high between Israel and Palestinians living in Gaza, the West Bank and East Jerusalem.
- According to Israel, allowing Palestinians to return to their homes would overwhelmingly threaten its existence as a Jewish state. (Israel is the only Jewish state in the world).
- The whole of Jerusalem is claimed by Israel as its capital. Palestinians claim East Jerusalem as the capital of a future Palestinian state.
- Though Israel does not recognise Palestine as a state, over 135 UN member countries do.
- In 1988, India became one of the first countries to recognize the Palestinian State.
Israel Palestine Conflict Latest Developments
The renewed violence in the region started on May 6, 2021 when Palestinians protested against an anticipated decision of the Israeli Supreme Court over the eviction of six Palestinian families from Sheikh Jarrah in occupied East Jerusalem. The next day, Israeli Police stormed the Al Aqsa mosque. A few days later, Hamas and other Palestinian groups started firing rockets from Gaza into Israel to which Israel retaliated.
Significance of Jerusalem
Jerusalem is an ancient city and claimed by both Israel and Palestine as their own. Israel claims the whole undivided city as its rightful capital while Palestinians refute this, stating their right of freedom and self-determination. The city is also considered a holy one having many places of religious importance to the three Abrahamic religions of Judaism, Christianity and Islam.
- Jerusalem was divided into two – western and eastern parts after Israel declared its independence in 1948.
- West Jerusalem became Israel’s capital while East Jerusalem became part of Jordan.
- In the Six-Day War in 1967, Israel captured East Jerusalem, among others.
- Shortly after the Israeli takeover, East Jerusalem was absorbed into West Jerusalem, together with several neighbouring West Bank villages.
- The same year, the UN passed a resolution asking Israel to retract from occupied places.
- In 1980, the Knesset (Israeli Parliament) passed the Jerusalem Law that declared that “Jerusalem, complete and united, is the capital of Israel”.
- Much of the international community considers Israel’s occupation of East Jerusalem as illegal.
- While both Israel and Palestine declared Jerusalem their capital, the Palestinians usually refer to East Jerusalem as the capital of the State of Palestine.
- In 2017, the then US President Donald Trump recognised the whole of Jerusalem as the capital of Israel.

Jerusalem is significant for both Jews and Muslims, as well as, Christians.
- The Old City of Jerusalem is in East Jerusalem. It has four quarters – Muslim, Jewish, Christian and Armenian.
- The city is significant for the Jews chiefly since it was the capital of the ancient Kingdom of Israel established by the biblical King David.
- Also, the First Temple was believed to have been built by King Solomon there, although there is no archaeological evidence of this.
- The Old City also contains the Western Wall, which was originally built as part of the Second Temple. This place is sacred for Jews.
- For Muslims, Jerusalem is the third holiest city after Mecca and Medina.
- The third holiest site for Muslims, the Al-Aqsa Mosque, is in the Old City.
- Muslims believe that Prophet Mohammad was transported to this place from Mecca during the ‘Night Journey’.
- For Christians also, the city is significant as in it is the Church of the Holy Sepulchre.
- It contains the two holiest sites in Christianity, the place where Jesus Christ was crucified and the place of his empty tomb.
- Temple Mount, known as Haram al Sharif in Arabic, is a site holy to both Jewish and Muslim people. It is in the Old City.
- The present site includes the Western Wall, the Al Aqsa Mosque, the Dome of the Rock, and the Dome of the Chain.
- Currently, Israel controls the security in the Temple Mount area with control over who has access to the site, whereas the religious aspects are dealt with by the Jordanian Waqf. Only Muslims are allowed to pray at the Dome and the Al Aqsa Mosque (sites which are revered by Jews as well for various reasons), while Jews can pray at the Western Wall.
- Jerusalem is central to the peace talks between both groups as the holy sites are in the same land
Way forward
- The best solution is a “two-state solution” that would establish Palestine as an independent state in Gaza and most of the West Bank, leaving the rest of the land to Israel. Though the two-state plan is clear in theory, the two sides are still deeply divided over how to make it work in practice.
- One state solution (only Palestine or only Israel) is not a viable option.
- Road Map for Peace: The European Union, UN, US, and Russia had released a road map in 2003, which outlined a clear timetable towards a Palestinian state.
- The democratization of the Palestinian society through which new credible leadership can emerge is necessary.
- The need of the hour is to treat this conflict as an Israeli-Arab conflict rather Israel-Palestine. As we have seen, conflict is not only between Israel and Palestine but also with other Arab countries such as Egypt, Jordan, Iran, Syria etc. All of them should participate in the negotiations and the final agreement should be recognized formally by each one of them along with UN general assembly and security council.
- It is time for the international community to find a just and lasting peaceful solution to the World’s most intractable conflict soon
Be the first one to comment





