ForumIAS announcing GS Foundation Program for UPSC CSE 2025-26 from 19 April. Click Here for more information.
Source- This post on Alternate wetting and drying technique has been created based on the article “Vietnam farmers are reducing methane emissions by changing the way they grow rice” published in “The first post” on 23 April 2024.
Why in the news?
According to a Food and Agriculture Organisation report 2023, rice paddies contribute 8% of all human-made methane in the atmosphere. The Vietnam farmers are reducing methane emissions by employing alternate wetting and drying technique to grow rice.
About Alternate wetting and drying (AWD)
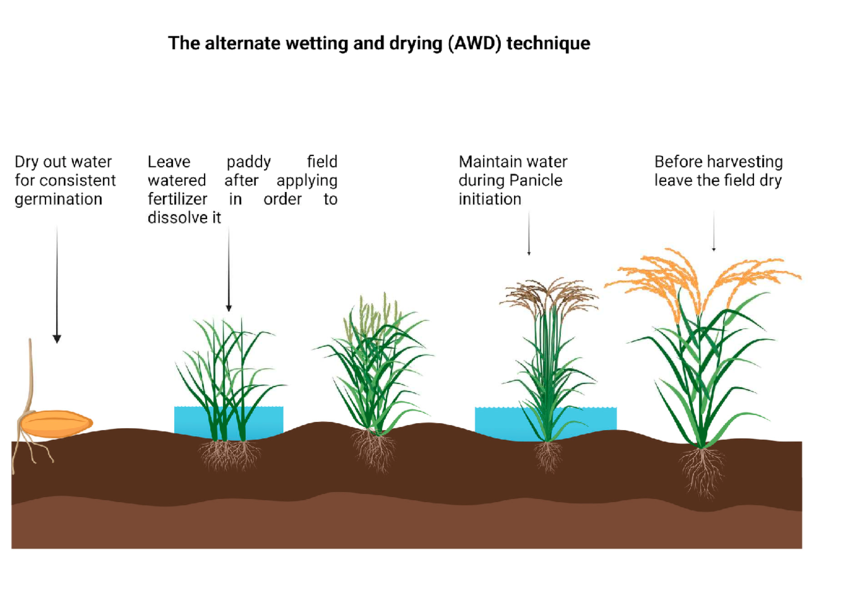
1. Alternate wetting and drying (AWD) is a water-saving technology that lowland (paddy) rice farmers can apply to reduce their water usage in irrigated fields.
2. In AWD, irrigation water is applied to flood the field a certain number of days after the
disappearance of ponded water.
Hence, the field is alternately flooded and dried.
3. The number of days of non-flooded soil in AWD between irrigations can vary from 1 day
to more than 10 days depending on the soil type.
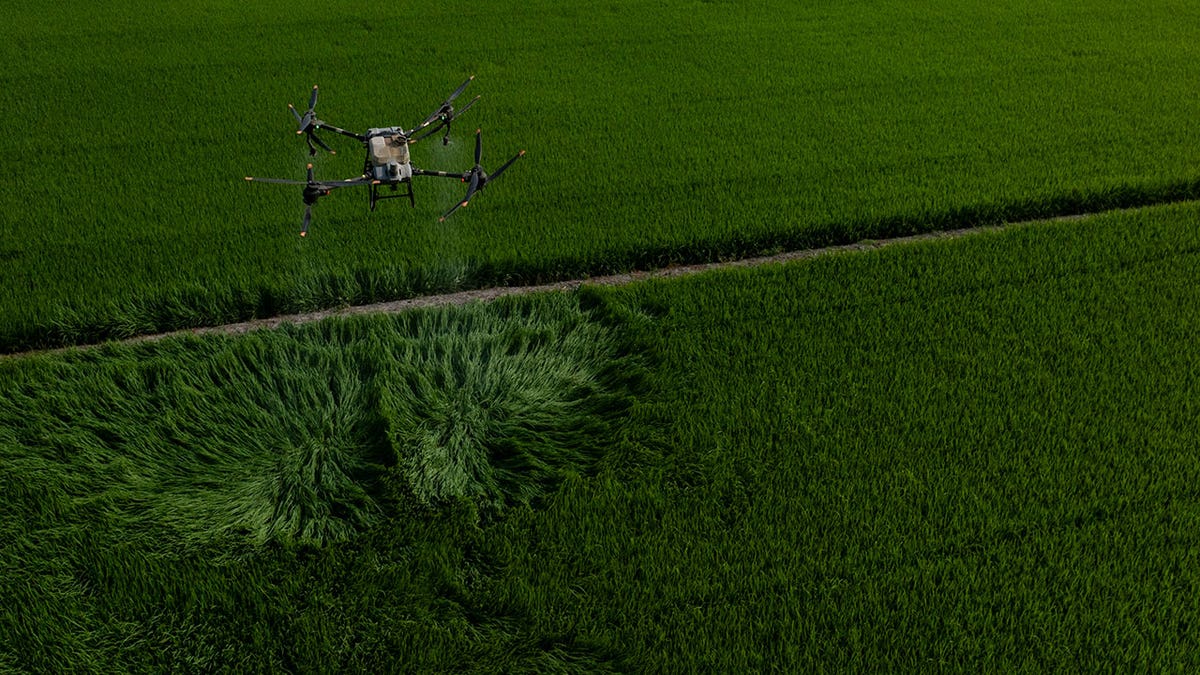
4. They also employ large drones to spray organic fertilizer onto the knee-high rice seedlings below.
Benefits of Alternate wetting and drying (AWD)

1. It produce less methane and thus environment friendly.
2. Using the drone to fertilize the crops saves on labour costs.
3. It also guarantees the precise application of fertilizers. Excessive amounts can lead to the release of nitrogen gases from the soil, contributing to Earth-warming effects.
UPSC Syllabus: Agriculture, Environment




