Source– This post on Stratospheric Aerosol Intervention (SAI) is based on the article “Climate impact: Water storage projected to decrease across wetter lands around Caspian, Mediterranean seas” published in “Down to Earth” on 26th February 2024.
Why in the News?
Recently, researchers studied the impact of stratospheric aerosol intervention (SAI) in mitigation of global warming effects in the region.
About stratospheric aerosol intervention (SAI)
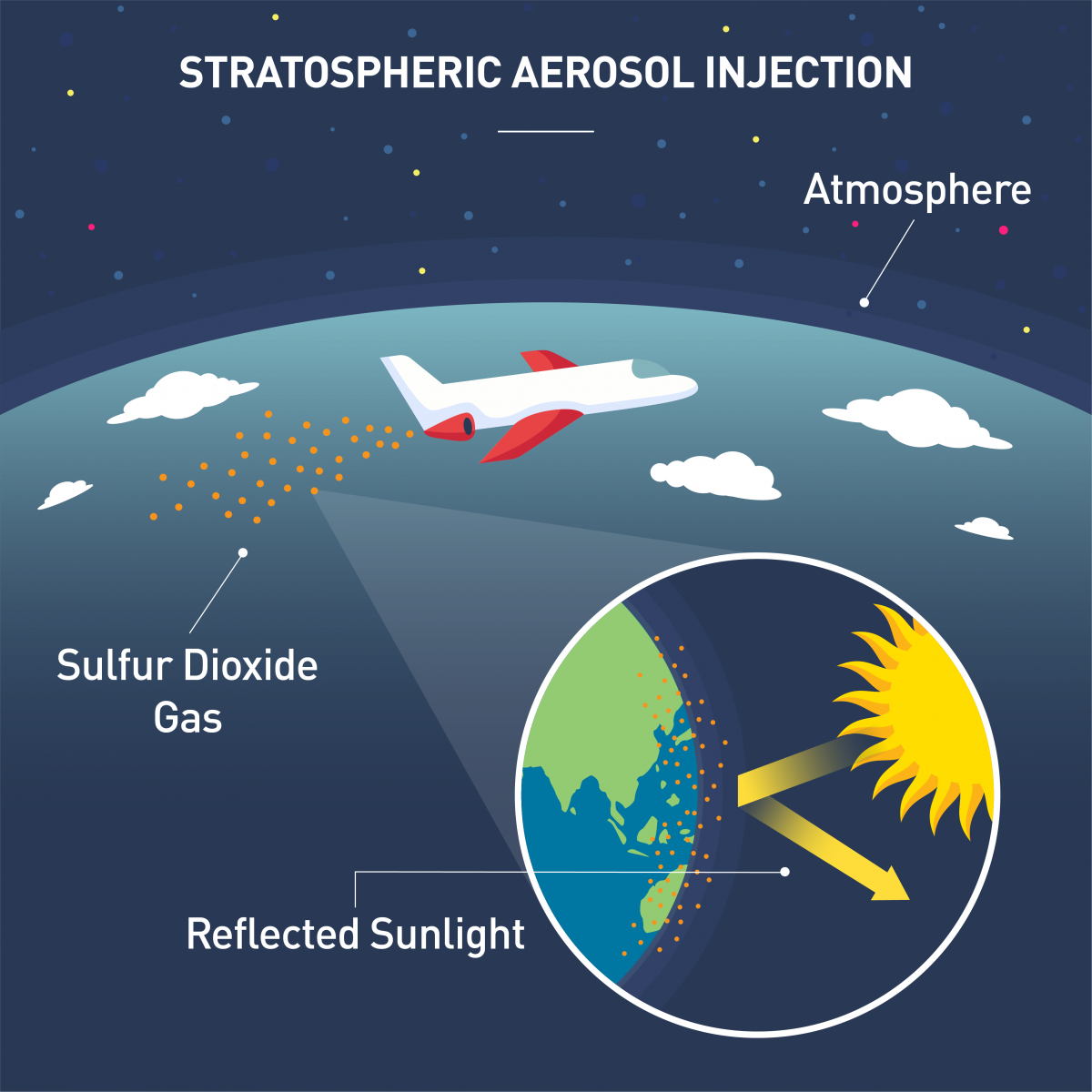
1) Description: Stratospheric Aerosol Intervention (SAI), also known as Stratospheric Aerosol Injection, is a geoengineering or climate engineering approach that aims to mitigate the effects of global warming.
2) Process: It is done by spraying large quantities of tiny reflective particles into the stratosphere to cool the planet by reflecting sunlight back into space.
3) Method: Method ranges from spraying reflective particles, such as sulphur dioxides, finely powdered salt or calcium carbonate. These are either sprayed from aircraft or are shot from artillery guns or large hoses to reach the sky.
5) Purpose: It aims to replicate the cooling impact of volcanic eruptions by introducing sulphur dioxide (SO2) directly into the stratosphere. Within the stratosphere, the SO2 transforms into sulfate aerosols that reflect sunlight.
6) As more radiation is scattered in the stratosphere by these aerosols, less solar energy is absorbed by the troposphere.
About Aerosols
1) A tiny solid or liquid particle suspended in air or as a gas is called aerosols.
2) Aerosols can be natural, such as fog or gas from volcanic eruptions, or artificial (anthropogenic), such as smoke from burning fossil fuels.
3) Aerosols are significant players in the global water cycle as they attract water vapour in the atmosphere, leading to the condensation of water molecules around particles such as dust, soot, salt, or ash.
UPSC Syllabus: Environment
Discover more from Free UPSC IAS Preparation Syllabus and Materials For Aspirants
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.







