Source: This post on Tardigrade Explaination has been created based on the article “Why ‘protected’ areas are seeing faster biodiversity decline” published in Indian Express on 26th October 2024.
Why in news?
Researchers have identified genetic mechanisms in a newly discovered species of tardigrade (Hypsibius henanensis) which enable it to withstand high levels of radiation.
These mechanisms protect and repair the microscopic animals’ DNA, making it a promising area of study for applications in space travel, nuclear pollution cleanup, and cancer treatment.
Key Findings
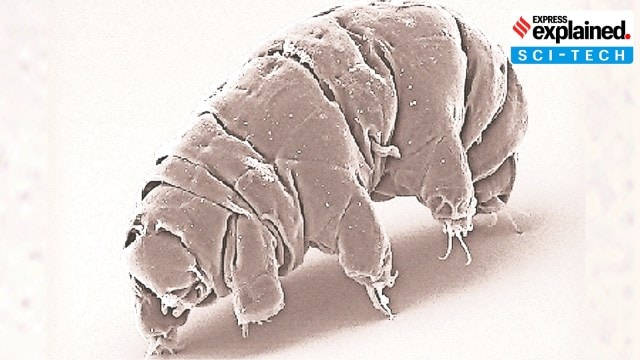
1. Discovery of Hypsibius henanensis: A new species of tardigrade was discovered from moss samples collected in Funiu Mountain, Henan province, China. This species, also known as the water bear, has 14,701 genes, of which 30% are unique to tardigrades.
2. Radiation Resistance Mechanisms
i) DNA Repair Genes: Researchers identified 2,801 genes associated with DNA repair. Specifically, three key mechanisms were found that aid in radiation resistance:
ii) Rapid DNA Repair: The protein TRID1 is utilized to swiftly repair double-strand breaks in DNA caused by radiation.
iii) Mitochondrial Proteins: Exposure to radiation activates a gene that produces proteins essential for mitochondrial synthesis, which also assist in DNA repair.
iv) Antioxidant Pigments (Betalains): This species produces betalains, antioxidant pigments that neutralize reactive chemicals formed inside cells due to radiation.
3. Potential Applications
i) Space Exploration: Insights from these mechanisms could help in developing protective measures against radiation for astronauts.
ii) Nuclear Cleanup: The same principles could assist in reducing radiation damage in environments affected by nuclear waste.
iii) Cancer Treatment: Betalains derived from Hypsibius henanensis were tested on human cells, showing improved survival rates post-radiation exposure, which could benefit patients undergoing radiation therapy.
4. Future Implications: This study opens possibilities for using tardigrade mechanisms to enhance stress tolerance in human cells, potentially advancing treatments for radiation exposure and offering protective measures for high-radiation environments.
UPSC Syllabus: Science and technology
Discover more from Free UPSC IAS Preparation Syllabus and Materials For Aspirants
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.







