Ensuring Infrastructure availability is a crucial aspect of the Industrial growth of a nation. In this section, we will cover all the updates issues and concepts related to the Infrastructure (roads, ports, airports, and railways) sector of India
Indian Vessels Act, 2021
Introduced: Lok Sabha (22nd Jul 2021)
Passed: Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha.
Present status: Received the assent of the President on the
11th August, 2021Contents
- 0.0.1 About Indian Vessels Act, 2021:
- 0.0.2 Key Features of the Indian Vessels Act, 2021:
- 0.0.3 About Inland Waterways:
- 0.0.4 About SilverLine Project:
- 0.0.5 Challenges:
- 0.0.6 About One Nation One Standard Mission:
- 0.0.7 Objectives of the One Nation One Standard Mission:
- 0.0.8 SDO Certification:
- 0.0.9 About Research Designs & Standards Organization(RDSO)
- 0.0.10 Benefits of SDO Recognition for RDSO:
- 0.0.11
- 0.0.12 What is the News?
- 0.0.13 What is Infrastructure Status?
- 0.0.14 Why this move?
- 0.0.15
- 0.0.16 What is the News?
- 0.0.17 Key Findings of the Roadmap for a Digitally Inclusive Bharat:
- 0.0.18 Inspiring Trust and Security in Digital Commerce
- 0.0.19 Preparing India’s Agri Enterprises for Connected Commerce
- 0.0.20 Digital Financial Inclusion:
- 0.0.21 Robust Transit Systems for Smart Cities
- 0.0.22 Introduction –
- 0.0.23 What are the key findings by the CEC panel?
- 0.0.24 What are the recommendations by the CEC panel?
- 0.0.25 Conclusion
- 0.0.26 What is the News?
- 0.0.27 About Railway’s Initiative
- 0.0.28 Railways Advisory:
- 0.0.29 Introduction-
- 0.0.30 Challenges during construction of Railway bride in Hilly areas
- 0.0.31 Examples of modern marvel of Indian Bridge-
- 0.0.32 What is the difference between Tallest Bridge and Highest Bridge?
- 0.0.33 What is the News?
- 0.0.34 What was the case?
- 0.0.35 What did the Supreme Court say?
- 0.0.36 About National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development (NBFID) Act,2021
- 0.0.37 Structure of the NBFID:
- 0.0.38 Objectives:
- 0.0.39 Functions:
- 0.0.40 Introduction
- 0.0.41 Background
- 0.0.42 Information about Great Nicobar Island
- 0.0.43 Current Scenario
- 0.0.44 About the Great Nicobar Development plan
- 0.0.45 Significance of the Great Nicobar Development plan
- 0.0.46 Concerns with the Great Nicobar Development plan
- 0.0.47 Suggestions
- 0.0.48 Conclusion
- 0.0.49 What is the News?
- 0.0.50 About DFIs:
- 0.0.51 Key Features of DFIs Development Finance Institution :
- 0.0.52 DFIs Development Finance Institution in India:
- 0.0.53 What is the news?
- 0.0.54 What is a Development Finance Institution(DFI)?
- 0.0.55 About Maitri Setu:
- 0.0.56 About Feni River:
- 1 Recent developments
- 2 Why Railways is in financial distress?
- 3 Suggestions
About Indian Vessels Act, 2021:
- Indian Vessels bill, 2021 seeks to replace the Inland Vessels Act, 1917. The bill aims to regulate the safety, security and registration of inland vessels.
Key Features of the Indian Vessels Act, 2021:
- Unified Law:
- The Bill provides for a unified law for the entire country, instead of separate rules framed by the States.
- This means that the certificate of registration granted under the proposed law will be deemed to be valid in all States and Union Territories.
- Moreover, there will also be no need to seek separate permissions from the States.
- Central Database of Vessels:
- The Bill provides for a central database for recording the details of the vessel, vessel registration, crew on an electronic portal. The Bill defines such vessels to include ships, boats, sailing vessels, container vessels, and ferries.
- Mandatory registration of Vessels:
- The bill requires all mechanically propelled vessels to be mandatorily registered.
- On the other hand, all non-mechanically propelled vessels will also have to be enrolled at the district, taluk or panchayat or village level.
- Prevention of pollution:
- Vessels will discharge or dispose sewage, as per the standards specified by the central government. State governments will grant vessels a certificate of prevention of pollution, in a form as prescribed by the central government.
About Inland Waterways:
- India has about 14,500 km of navigable waterways which comprises rivers, canals, backwaters, creeks among others.
- About 55 million tonnes of cargo are being moved annually by Inland Water Transport (IWT), in a fuel-efficient and environment-friendly mode.
About Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI):
- Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI) was constituted in 1986 for the development and regulation of inland waterways for shipping and navigation.
- Purpose: The Authority primarily undertakes projects for the development and maintenance of IWT infrastructure on national waterways. IWAI did this through the grants received from the Ministry of Shipping.
What is Kerala’s “SilverLine project”?
What is the News? Kerala cabinet has given the approval to begin acquiring land for the SilverLine Project.
About SilverLine Project:
- SilverLine Project is Kerala’s semi high-speed railway project that aims to reduce travel time between Kerala’s northern and southern ends.
- Distance: The railway line will be around 529 kms long, covering 11 districts through 11 stations. It will link the southern end and state capital Thiruvananthapuram with its northern end of Kasaragod.
- Implementation: The Kerala Rail Development Corporation Limited(KRDCL) will execute this project.
- KRDCL is a joint venture between the Kerala government and the Union Ministry of Railways.
- Significance of the Project: Once the project is completed, one can travel from Kasaragod to Thiruvananthapuram in less than four hours on trains travelling at 200 km/hr. The current travel time on the existing Indian Railways network is 12 hours.
- Duration of the Project: The deadline for the project is 2025.
Expected Benefits of SilverLine Project: As per the Government, the silver line project will:
- reduce greenhouse gas emissions
- help in expansion of Ro-Ro services
- produce employment opportunities
- integrate airports and IT corridors and
- faster development of cities it passes through.
Read more– Kerala Model to tackle Covid Pandemic
Challenges:
- Land Acquisition: The deadline for the project i.e. by 2025 is not realistic due to the challenging nature of land acquisition in a highly densely populated state like Kerala.
- Environment Cost: The environmentalists are opposing this project due to the potentially irreversible impact on the state’s rivers, paddy fields, and wetlands, triggering floods and landslides in the future on the proposed route.
Source: Indian Express
“One Nation One Standard Mission” and “Research Designs & Standards Organization”
What is the News?
Indian Railways Research Design & Standards Organization(RDSO) has become the nation’s first institution to be declared as Standard Developing Organization(SDO) under the “One Nation One Standard” mission.
Contents
About One Nation One Standard Mission:
- One Nation One Standard was first conceived in 2019 by the Bureau of Indian Standards(BIS).
- The mission is on the line of one nation, one ration card scheme in order to ensure quality products in the country.
Objectives of the One Nation One Standard Mission:
- To aggregate and integrate the existing capabilities in standardisation. Further, it will also provide dedicated domain-specific expertise available with various organizations in the country.
- This will enable one template of standard for one given product instead of having multiple agencies set it.
- To enable the convergence of all standard development activities in the country, resulting in One National Standard for One Subject. This will help in establishing a Brand India identity in the long run.
SDO Certification:
- To attain the One Nation One Standard vision, BIS launched the Standard Developing Organization(SDO) recognition scheme.
- The recognition is valid for 3 years and will require renewal after completion of the validity period.
About Research Designs & Standards Organization(RDSO)
- RDSO is the sole R&D Wing of the Ministry of Railways. It was founded by integrating the Central Standards Office (CSO) and the Railway Testing and Research Centre(RTRC) into a single unit in 1957.
- Purpose: It is one of India’s leading Standard formulating bodies undertaking standardization work for the railway sector.
- Location: It is situated in Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh.
Read Also :-The International Labour Organization
Benefits of SDO Recognition for RDSO:
- RDSO will be recognized on international standards-making bodies and there will be integration with global supply chain/global trade
- The competitiveness amongst the industry will increase
- There will be a reduction in cost and quantum improvement in the quality of product and services
- There will be smooth induction of the latest evolving & emerging technologies on Indian Railways
- Dependence on imports will reduce and “Make-in-India” will get a boost
- Improved ease-of-doing-business.
Source: Financial Express
“Mekedatu Project” – A Panel to investigate charges of illegal construction
What is the News?
The National Green Tribunal(NGT) has formed a committee to investigate the alleged violation of norms in the construction of the Mekedatu project across the Cauvery river. The NGT has also directed the panel to submit a report on or before July 5.
About Mekedatu Project:
- Mekedatu project is a balancing reservoir and drinking water project. It is to be built at the confluence of the Cauvery and Arkavathi rivers by the Karnataka Government.
- Purpose: The project aims to solve the drinking water problems of the Bengaluru and Ramanagara district. It would also generate 400 MW of hydroelectric power.
- Dispute: The Tamil Nadu Government has objected to the project saying Karnataka had not sought prior permission for the project.
- Tamil Nadu has also filed a petition in the Supreme Court in 2018 seeking a stay on the project.
Objections by Tamil Nadu Government:
- Firstly, the Mekedatu project would affect the flow of Cauvery water to Tamil Nadu.
- Secondly, Karnataka has no right to construct any reservoir on an inter-state river without the consent of the lower riparian state i.e. Tamil Nadu in this case.
- The project is also against the final order of the Cauvery Water Disputes Tribunal (CWDT). During that, the SC held that no state can claim exclusive ownership or assert rights to deprive other states of the waters of inter-state rivers.
- Thirdly, The CWDT and the SC have found that the existing storage facilities available in the Cauvery basin were adequate for storing and distributing water. So, the Tamil Nadu Government is demanding outright rejection of the project.
Other concerns with the project:
- Almost 63% of the forest area of the Cauvery Wildlife Sanctuary will be submerged in the project.
Source: The Hindu
Finance Ministry grants “infrastructure status for convention centres”
What is the News?
The Finance Ministry has granted infrastructure status for exhibition and convention centres. The expectation from this move is to ease bank financing for such projects.
What is Infrastructure Status?
- The Department of Economic Affairs(DAE), Ministry of Finance will grant the Infrastructure Status.
- Benefits: The status helps projects in such sectors to get easier financing from banks. However, the status no longer involves significant tax breaks.
Infrastructure Status for convention centres:
- Firstly, The government included ‘Exhibition-cum-Convention Centre in the Harmonised Master List of Infrastructure. This is done by creating a new category under Social and Commercial Infrastructure.
- Secondly, however, The benefits are not available to all convention centres. The benefits will be available only for projects with a minimum built-up floor area of 1,00,000 square metres with exclusive exhibition space or convention space or both combined.
- Thirdly, these include primary facilities such as exhibition centres, convention halls, auditoriums, plenary halls, business centres, meeting halls among others.
Why this move?
- India doesn’t have large convention centres or single halls with capacities to hold 7,000 to 10,000 people.
- On the other hand, countries such as Thailand are a major global MICE (Meetings, Incentives, Conferences and Exhibitions) destination.
- Hence, granting infrastructure status will help the sector to generate significant financing for the projects.
Note: In August 2020, the Government of India had granted ‘Infrastructure’ status for affordable rental housing projects.
Source: The Hindu
Central Vista Project – Demolition of National Institutions
Synopsis: Demolition of national institutions for Central Vista Project require thorough analysis.
Introduction
- The Government of India’s Central Vista redevelopment project is being treated as a national priority amid a pandemic. This is very debatable. The project comprises the construction of a new Parliament building and new residences for the Prime Minister and the Vice President.
- A new Parliament building is certainly required. There is a strong case for restructuring the existing offices of the central government. However, it is not the right time for giving priority to a development project over public good.
- Moreover, 76 scholars, artists, writers, curators, and museum professionals highlighted a major concerning facet of the project last week. The National Museum of India, the Indira Gandhi National Centre for the Arts (IGNCA), and the National Archives are set to be smashed to make way for new buildings.
Why there has been criticism of demolition of national institutions?
- Firstly, these experts have asked for a speedy suspension of the project. Their concern is valid about the preservation of the collections kept at these centers.
- Secondly, transfer of the materials at the National Museum, archival accounts at the National Archives, and manuscript holdings at the IGNCA can be a very perplexing task. It is a difficult task that needs thorough planning and knowledge.
- Thirdly, such major changes around chief institutions take place only after extensive talks in any part of the world. Not in an opaque and casual manner as it is being planned here.
- Fourthly, the experts have pointed out that articles at the National Museum still lack a complete inventory. This could lead to a risk of loss or mishandling.
- Lastly, the Central Vista redevelopment project is clearly being implemented in a hurry. The government’s intolerance towards any public analysis of the project is evident. They have even banned the photography of the construction.
The country is facing an unmatched health crisis. The impact of the crisis can also be felt on the economic, social, and political spheres. The government should suspend the project, and take the Opposition and the public into confidence on the future course, in calmer times.
Source: Click here
Central Vista judgment: Issue of public participation in public projects
NITI Aayog’s Report on Creating a “Roadmap for Digitally Inclusive Bharat”
Contents
What is the News?
NITI Aayog and Mastercard have released a report titled ‘Connected Commerce: Creating a Roadmap for a Digitally Inclusive Bharat’.
Purpose of the report: The report identifies challenges in accelerating digital financial inclusion in India. The report also provides recommendations for making digital services accessible to its 1.3 billion citizens.
Key Findings of the Roadmap for a Digitally Inclusive Bharat:
Enabling Global Opportunities for MSMEs
- MSMEs have been a key growth driver for the Indian economy. This sector has employed some 110 million people or over 40% of India’s non-farm workforce.
- However, the lack of proper documentation, bankable collateral, credit history and non-standard financials force them to access informal credit. Also, the informal credit interest rates are double that of the formal lenders.
- Suggestion:
- Digitize registration and compliance processes and
- Diversify credit sources to enable growth opportunities for MSMEs.
Inspiring Trust and Security in Digital Commerce
- Firstly, there has been tremendous growth in digital payments in the past few years.
- Secondly, the surge in digital transactions has also increased the risk for possible security breaches, both for consumers and businesses.
- Thirdly, a Medici report of June 2020 says 40,000 cyber-attacks targeted the IT infrastructure of the banking sector in India.
- Suggestion:
- Build information sharing systems including a ‘fraud repository’.
- Ensure that online digital commerce platforms carry warnings to alert consumers to the risk of frauds.
Preparing India’s Agri Enterprises for Connected Commerce
- Agriculture with its allied sectors provides livelihood to a large section of the Indian population. Over the years, agriculture’s contribution to national GDP has declined from 34% in 1983-84 to just 16% in 2018-19.
- However, most agri-techs have not succeeded in digitizing financial transactions for farmers. Also, they failed to enable formal credit at lower rates of interest by leveraging transaction data.
- Suggestions:
- Enable agricultural NBFCs to access low-cost capital and deploy a ‘phygital’ (physical + digital) model for achieving better long-term digital outcomes.
- Digitizing land records will also provide a major boost to the sector.
Digital Financial Inclusion:
- A lot of effort and success has been on the supply side of DFI. For example, initiatives like E-Governance initiatives, JAM trinity, Direct Benefit Transfer(DBT) among others.
- However, the success in the digital financial flow comes at the last mile where account holders mostly withdraw cash for their end-use.
- Suggestion:
- Strengthen the payment infrastructure to promote a level playing field for NBFCs and banks.
Robust Transit Systems for Smart Cities
- The transport sector is expected to grow to 12% of GDP by 2026.
- Hence, there is a huge opportunity for the government and private sector to collaborate and provide top-quality systems for mass transit.
- Suggestions:
- Make city transit seamlessly accessible to all. Transit has to include visitors, migrant workers from towns or villages also. The government can allow price benefits of digital payments to poor citizens
- Leverage existing smartphones, cards and non-transit payment modes as far as possible.
Source: PIB
GOA Infra Project Red Flagged- Key Findings and Recommendation by the CEC Panel
Synopsis – The Supreme Court-appointed Central Empowered Committee (CEC) recommended changes to the rail track doubling project in GOA. The project would have destroyed the fragile ecosystem of Western Ghats.
Contents
Introduction –
- The Standing Committee of the National Board for Wildlife (SC-NBWL) gave clearance to linear infrastructure projects within the boundaries of Wildlife Sanctuary and National Park in Goa.
- The Goa Foundation filed an application against this decision before SC -CEC.
- The CEC examined the proposal cleared by the SC-NBWL for the three linear projects in Goa —
- Doubling of railway tracks.
- Four laning of a nationwide freeway.
- Goa Tanmar Transmission Project.
- These Projects included the diversion of about 170 hectares of forest land and sanctuary land, and the felling of an estimated 37,000 trees. It was impacting the Bhagwan Mahaveer Wildlife Sanctuary (BMWS) and Mollem National Park (MNP) in Goa [Western Ghats].
What are the key findings by the CEC panel?
- Environment impact- The project will destroy the Western Ghats ecosystem, which is one of the country’s most valuable wildlife corridors. It is also a globally recognized biodiversity hotspot.
- Not justifiable- The doubling of railway tracks will only marginally enhance the capacity of the most inefficient section of the railway network.
- The estimate by the railways is not based on facts, despite the change in policy on the import of coal.
- Difficulty in animal movement- The wider openings through the Western Ghats will further fragment the habitat and will make the movement of wildlife across the railway line much more difficult and dangerous.
- The width of underpasses/overpasses in the proposal, providing for the free movement of wildlife animals, was also inadequate.
What are the recommendations by the CEC panel?
Following are the recommendations by the apex court-appointed panel –
- Revocation of approval granted by SC-NBWL for doubling of the railway tracks that run through the ecologically sensitive Western Ghats.
- Re-alignment of the Goa Tamnar Transmission Project: The CEC also recommended redrawing and modify the alignment for Goa Tamnar power transmission project, this will help in-
- Protecting forest cover in order to make way for the 400 KV line.
- Protecting wildlife- The CEC suggested an elevated structure at strategic locations leaving the surface terrain free for movement of all types of wildlife.
- Furthermore, the project of making four lanes of existing NH-4A needs to obtain environment clearance [EC] under Environment Impact Assessment notification, 2006.
Conclusion
The implementation of recommendations in the proposal would be beneficial. It would aid in the conservation of the valuable forest cover and wildlife in the ecologically fragile and biodiversity-rich Western Ghats.
Source – The Indian Express
Railways to Map Local Festivals Near Tracks
What is the News?
The Ministry of Railways will map local festivals celebrated along the railway tracks across the country. It aims to stop the unusual incidents resulting in casualties.
About Railway’s Initiative
- People in India celebrate several local festivals near Railway tracks. During this, the crowd gathers near the railway premises and crosses the track in groups to take part in the event.
- Such occasions resulted in casualties in the past.
- Example: In a previous year, 61 people killed when a crowd was watching a burning ‘Ravana’ effigy as part of the Dasara celebrations near Amritsar. During the festival, People were crossing the railway track and a high-speed train ran over them.
Read Also–Food security in india
Railways Advisory:
- Indian Railways advised all divisional railway managers to prepare a list of local festivals. The list will contain all such festivals that create the possibility of crowds gathering on and around railway tracks in all States.
- The loco pilot of all trains passing through such locations on the festival day would receive suitable advice. It would contain speed restrictions and other safety aspects.
Source: The Hindu
Chenab Bridge – An Icon of Indian Railways Heritage
Synopsis – Indian Railway is building modern engineering marvels such as Chenab Bridge and Anji Khad Bridge. Decades from now, they will serve as the Railways’ heritage.
Contents
Introduction-
- Over the last 160 years, railway engineers built a number of ‘Mega Structures,’ including railway bridges.
- The Indian Railway has 1,50,390 Bridges, out of which 702 are important, 12,256 major and 1,37,432 minor bridges.
- According to 2015 CAG report there are 36,470 Bridges which are more than 100 years old and 6,680 Bridges more than 140 years old.
- Causey Arch in England, designed in 1725-26, is the world’s oldest surviving railway bridge.
Challenges during construction of Railway bride in Hilly areas
Tough Terrain- Bridge building in a hilly area presents its own set of challenges. The climatic conditions, geological features, and hydrological parameters differ greatly in a hilly environment. It makes construction conditions difficult.
- Deep gorges, severely cold temperatures, rivers with bouldery beds, strong winds, landslides are some example of obstacles in building bridges in hilly areas.
Examples of modern marvel of Indian Bridge-
- One, Irang Bridge – In Manipur, Indian Railways is building the world’s tallest pier bridge across the river Ijai. The pier bridge will be 141 metres tall surpassing the existing record of 139 metres of the Mala-Rijeka Viaduct in Europe.
- Two, New Pamban bridge – Indian Railways first vertical lift rail-sea bridge. The New Pamban Bridge will be over 2 kilometers long when completed. It will allow ships and steamers to pass.
- Three, Bogibeel Bridge – Bogibeel Bridge, on the Brahmaputra River in Assam, is India’s longest rail-road bridge.
- Four, Chenab Bridge – Across the Chenab river, the world’s highest steel arch bridge is being built. It has a height of 359 metres from the bed level to the centre of the arch. Chenab Bridge will term as a future icon of Indian Railways heritage.
What is the difference between Tallest Bridge and Highest Bridge?
- Tallest Bridge – Distance from the highest portion of the bridge to the surface of the water.
- Highest Bridge- The highest Bridge is defined in terms of deck height. The deck height of a bridge is the maximum vertical drop distance between the bridge deck and the ground or water surface beneath the bridge span.
Source- Indian Express
Railways Completes Arch Closure of “Chenab bridge”
What is the News? The Indian Railways completes the Arch closure of the iconic Chenab Bridge.
About Chenab Bridge:
- Chenab Bridge is an Indian railway steel and concrete arch bridge. It is under the construction between Bakkal and Kauri in the Reasi district of Jammu and Kashmir.
- Length: The bridge is being constructed over the Chenab River. It is 1315 m long and at a height of 359 m over the river bed level.
- Part of: The bridge is a part of 272 km Udhampur-Srinagar-Baramulla rail link project(USBRL). The Northern Railway is constructing it.
- Features:
- The steel arch is an important part of the bridge. It consists of steel boxes. It will be filled with concrete to improve stability.
- The bridge will be able to withstand earthquakes with a magnitude of up to eight and high-intensity blasts.
- The bridge can withstand high wind speeds up to 266 km per hour.
- Significance: Once completed, the bridge will be the World’s highest railway bridge.
Source: The Hindu
SC Issues Directions for “Accident Information Report”
What is the News?
The Supreme Court issues directions to police, Motor Accidents Claims Tribunals(MACTs), and insurance companies regarding accident information reports. The aim of the directions is to make the compensation process to victims more smooth and claimant-friendly.
What was the case?
- The Insurance company Bajaj Allianz filed a writ petition in the Supreme Court. The petition raised the issue of the difficulty of accident victims, waiting for years for compensation.
- Bajaj Allianz said that the police take months to even file an accident report for submission before the Motor Accidents Claims Tribunals(MACTs). This is the norm in many parts of the country,
What did the Supreme Court say?
The Supreme Court issued directions to prevent delays in the disbursement of compensations to victims. The police, motor accident claims tribunals and insurers across the country have to uniformly practice these directions:
- Firstly, Accident Information Report: The jurisdictional police station shall report the accident under Section 159 of the Motor Vehicle Act. Further, the police need to send the report of the accident to the tribunal and insurer within the first 48 hours.
- Secondly, Detailed Accident Report: Police shall collect the documents relevant to the accident. This includes documents for computation of compensation and verification of the information and documents. This report shall be emailed to the tribunal and the insurer within three months.
- Thirdly, the tribunal shall issue summons along with the Report or the application for compensation to the insurer by email.
- Fourthly, the insurer shall email their offer for settlement/response to the Report to the tribunal.
- Fifthly, after passing the award, the tribunal shall email an authenticated copy of the award to the insurer.
- Sixthly, the insurer shall satisfy the award by depositing the awarded amount into a bank account maintained by the tribunal by RTGS or NEFT.
Further, the Supreme Court has also ordered the Centre to launch a national online platform. The platform could be operated and accessed across the country for submission of accident reports, claims and responses to claims. This would end the distress felt by victims during accidents that happened in places other than their native State.
Source: The Hindu
National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development Act, 2021
Introduced: The Bill was introduced in Lok Sabha on 22/03/2021 as a Government Bill (Ministry of Finance, Corporate Affairs and Information & Broadcasting).
Present Status: The Bill was passed in both the Houses and received President’s assent on 28.03.2021.About National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development (NBFID) Act,2021
- Aim: The Act seeks to establish the NBFID as the principal development financial institution(DFIs) for infrastructure financing.
- DFIs are set up for providing long-term finance for segments involving risk beyond the acceptable limits of commercial banks and other ordinary financial institutions.
Click Here to Read About Development Financing Institution(DFIs)
Structure of the NBFID:
- NBFID will be a corporate body with authorised share capital of Rs. 1 lakh crores.
- Initially, the central government will own 100% shares of the institution. This share may subsequently be reduced up to 26%.
Objectives:
- Financial Objective: To directly or indirectly lend, invest, or attract investments for infrastructure projects located entirely or partly in India.
- Developmental Objective: Includes facilitating the development of the market for bonds, loans, and derivatives for infrastructure financing.
Functions:
NBFID will work toward financial as well as developmental objectives.
Financial Functions include:
- Firstly, extending loans and advances for infrastructure projects.
- Secondly, taking over or refinancing such existing loans.
- Thirdly, attracting investment from private sector investors and institutional investors for infrastructure projects.
- Fourthly, organising and facilitating foreign participation in infrastructure projects.
- Fifthly, facilitating negotiations with various government authorities for dispute resolution in the field of infrastructure financing.
- Lastly, providing consultancy services in infrastructure financing.
Developmental functions include:
- Facilitating the development of the market for bonds, loans, and derivatives for infrastructure financing
Management of NBFID:
- A Board of Directors will govern the NBFID. The Chairperson will be appointed by the central government in consultation with RBI.
Source of funds:
- NBFID may raise money in the form of loans or otherwise both in Indian rupees and foreign currencies. It may also raise finances by the issue and sale of various financial instruments including bonds and debentures.
- NBFID may also borrow money from: (i) central government, (ii) Reserve Bank of India (RBI), (iii) scheduled commercial banks, (iii) mutual funds, and (iv) multilateral institutions such as the World Bank and Asian Development Bank.
Support from the central government:
- The central government will provide grants worth Rs 5,000 crore to NBFID by the end of the first financial year.
- The government will also provide a guarantee at a concessional rate of up to 0.1%. This facility will be available for borrowing from multilateral institutions, sovereign wealth funds, and other foreign funds.
The prior sanction for investigation and prosecution:
- No investigation can be initiated against employees of the NBFID without the prior sanction of:
- the central government in case of the chairperson or other directors, and
- managing director in case of other employees.
- Courts will also require prior sanction for taking cognizance of offences in matters involving employees of NBFID.
Other DFIs:
- The Act also provides for any person to set up a DFI by applying to RBI.
- RBI may grant a licence for DFI in consultation with the central government. RBI will also prescribe regulations for these DFIs.
NITI Aayog’s Great Nicobar Development plan – Explained, Pointwise
Contents
Introduction
NITI Aayog’s Great Nicobar Development plan aims to promote the holistic development of Greater Nicobar. Based on that, the Standing Committee of the National Board for Wildlife (NBWL) denotified the entire Galathea Bay Wildlife Sanctuary for building port and other related infrastructure.
This would facilitate the realization of NITI Aayog’s master plan for the development of the great Nicobar island. However, experts have expressed concern that this rapid development can lead to disastrous consequences.
Background
- The Island Development Agency(IDA) was constituted in 2017 under the aegis of the Ministry of Home Affairs. The IDA looks into the holistic development of islands.
- Home Minister of India is its chairman. CEO of NITI Aayog acts as its convener.
- The other members of IDA include Secretary- Tourism, Tribal affairs, the Home Secretary, Secretary Ministry of Environment, and Cabinet secretary.
- NITI Aayog has been mandated with the task to steer the holistic development of the islands sustainably. The program aims to attain sustainable development in the identified Islands without damaging the pristine biodiversity.
- In this regard, the NITI Aayog came up with a Great Nicobar Development plan.
Information about Great Nicobar Island
- Great Nicobar is the southernmost and largest of the Nicobar Islands of India. The island of Sumatra has located 180 km to the south of Great Nicobar. It has an area of about 1045 sq. km.
- According to the 2011 census, it has a population of about 8,069. The island is home to one of the most primitive tribes of India — the Shompens.
- The island includes the Great Nicobar Biosphere Reserve (GNBR) comprising the Galathea National Park and the Campbell Bay National Park.
- Indira Point in the Great Nicobar Island is the southernmost point of India’s territory.
Current Scenario
- The National Board for Wildlife (NBWL) denotified the entire Galathea Bay Wildlife Sanctuary.
- The sanctuary is one of the ‘Important Coastal and Marine Biodiversity Areas’. Further, it is also an ‘Important Marine Turtle Habitats’ in the country as per National Marine Turtle Action Plan.
- Another Environment Ministry expert committee approved a “zero extent” Ecologically Sensitive Zone (ESZ) for the Galathea National Park. This would allow the use of land in the south-eastern and south-western parts of the island for the Great Nicobar Development plan.
About the Great Nicobar Development plan
- Firstly, The overall Great Nicobar Development plan envisages the use of about 244 sq. km. region for development purposes.
- Secondly, Phase 1 of the plan will cover:
- 22 sq. km. airport complex,
- Transshipment port (TSP) at South Bay
- Parallel-to-the-coast mass rapid transport system and
- Free trade zone and warehousing complex on the southwestern coast.
- Thirdly, Andaman and Nicobar Islands Integrated Development Corporation (ANIIDCO) will be the nodal agency for the implementation of the Great Nicobar Development plan.
Significance of the Great Nicobar Development plan
- Job opportunities for locals: The plan involves the creation of infrastructure (ports, airports, etc.). This will help in creating satisfactory jobs for the locals.
- Economic Development: It will help in creating tourism prospects in the region. This will aid the income generation in the region.
- The per capita income in Andaman & Nicobar Islands for the year 2015-16 was Rs. 1,24,361. This was much lower than the per-capita income of other Union Territories (Chandigarh, Delhi, and Puducherry.)
- Connectivity: The development of world-class infrastructure will help in improving inter-island connectivity. Thereby, improving governance and boosting export potential.
- Social Benefits: It would further create affordable state-of-the-art facilities for healthcare, quality education, and adequate air, sea and web infrastructure.
- It will facilitate the delivery of e-governance services such as telemedicine and tele-education, as a part of the Digital India initiative.
- Strategic benefit: The Nicobar island located in proximity to the strait of Malacca. This demands the creation of robust infrastructure for meeting geopolitical interests in the region.
- The islands are also home to India’s only tri-services command – the Andaman and Nicobar Command (ANC).
- The command holds immense relevance due to rising Chinese aggression in the Indo-Pacific region.
Concerns with the Great Nicobar Development plan
- Firstly, a threat to biodiversity: Any construction in the region threaten the survival of certain important organisms. Such as,
- The beaches at the mouth of the river Galathea in South Bay are among the most prominent nesting sites of Giant leatherback turtles.
- Similarly, 90% of the Nicobar megapode’s nesting sites are within a distance of 30 m from the shore.
- Secondly, jeopardizing environment for economics: Galathea sanctuary lies in Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ)-I (the zone with maximum protection). But still, a slew of high-value projects got precedence over the pristine biodiversity.
- Thirdly, neglecting tribal rights: The proposed project areas are important grounds for the hunter-gatherer nomadic community especially Shompen. Initiation of work would make large forest areas inaccessible and useless for the Shompen.
- Fourthly, geological volatility: Andaman & Nicobar Islands are located in seismic zone V. Further, The Andaman & Nicobar observe frequent storms and cyclones. This can easily destroy constructed structures.
- For instance, In 2004 Tsunami caused a 3-4 metre land subsidence. This is the reason for the submergence of a lighthouse located at Indira point.
- Fifthly, undermining international obligations: The Galathea Bay Wildlife Sanctuary forms part of a UNESCO World Heritage Site. So preservation of this pristine biodiversity is an International Obligation of India.
- And lastly, information Deficit: The rationale, process of creation, and other relevant provisions of the plan are still not publicly available.
Suggestions
- Firstly, the work must be carried out with due regard to tribal rights. This would involve proper adherence to policies like the Shompen Policy of 2015.
- The Shompen Policy of 2015 calls for giving priority to tribal rights over large scale development proposals.
- Secondly, any construction under the Great Nicobar Development plan should involve a proper Environment impact assessment (as mandated by the Environment Protection Act 1986). This will make development more feasible. Further, It will minimise the threat of excessive environmental degradation.
- Thirdly, construction of infrastructure should be done using eco-friendly practices like strict adherence to GRIHA code for building construction.
- GRIHA means Green Rating for Integrated Habitat Assessment. It is the National Rating System of India.
- It has been conceived by TERI and developed jointly with the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy, Government of India.
- Fourthly, NITI Aayog and the agencies participating in planning should maintain transparency in data. The government should release the data on the rationale, the process of creation, consulted groups etc. in public domain. This will give a holistic view to critics and supporters.
- Finally, India should enhance Cooperation with countries like Japan, South Korea etc. This will help in developing successful island development models.
Conclusion
India needs to achieve the Vision of “Happy and Prosperous Islanders on ecologically-protected Islands”. To achieve that, India needs to adopt development plans that are technically feasible, economically profitable and socially acceptable.
- The Island Development Agency(IDA) was constituted in 2017 under the aegis of the Ministry of Home Affairs. The IDA looks into the holistic development of islands.
What are “DFIs or Development Finance Institutions”?
Contents
What is the News?
The Union Cabinet has approved a bill to set up a DFI (Development Finance Institution). It will be called National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development (NaBFID).
Click Here to Read about NaBFID
About DFIs:
- The development finance institutions(DFI) are usually owned by the government or public institutions. DFIs provide funds for infrastructure and large-scale projects. Large Scale banks are often not interested in lending for such projects due to viability issues.
- The prime objective of DFI is the economic development of the country via financing infrastructure activities.
- Their cost of borrowings also reduces because of the attached government guarantees.
- Setting up of DFI is important due to rising NPAs in commercial banks. At present, they are unable to finance infrastructure projects in India.
Key Features of DFIs Development Finance Institution :
- Funding: DFIs do not accept deposits from people. Thus, they raise funds by borrowing from governments, insurance companies, and sovereign funds.
- Functions: They provide technical assistance like project report, viability study, and consultancy services.
- DFIs provide credit enhancement for infrastructure and housing projects. It also helps in improving debt flows towards infrastructure projects.
- DFIs strike a balance between public good via infrastructure and profit maximization. It often prioritizes the former over the latter.
DFIs Development Finance Institution in India:
- The first DFI in India was the Industrial Financial Corporation of India (IFC) that was launched in 1948. IDBI, UTI, NABARD, EXIM Bank, SIDBI, NHB, IIFCL are the other major DFIs.
- Later, several of them were converted into banks like ICICI Bank, IDBI Bank etc.
DFI categories: DFIs in India are classified into four categories of institutions as per their functions:
- National Development Banks e.g IDBI, SIDBI, ICICI, IDFC
- Sector specific financial institutions e.g. EXIM Bank, NABARD, NHB
- Investment institutions e.g LIC, GIC, UTI
- State level institutions e.g. state Finance corporations.
Source: The Hindu
Cabinet Clears Proposal for Setting up of “Development Finance Institution (DFI)”
What is the news?
The Union Cabinet approved a bill to set up a Development Finance Institution(DFI). It will be called National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development (NaBFID).
About National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development (NaBFID):
- Owned by: Initially, the Government of India will own it with a 100% stake. It will gradually be brought down to 26% in a few years.
- Purpose: It will provide finance for social and economic infrastructure projects identified under the National Infrastructure Pipeline(NIP).
- Managed by: A professional board with at least 50 percent of the members as non-official directors.
- Capital Infusion: The capital infusion by the Government will be Rs 20,000 crore with an initial grant of Rs 5,000 crore. It is then expected to raise around Rs 3 lakh crore in the next few years by Market funds.
- Tax Exemption: The government will provide a 10-year tax exemption to funds invested in the DFI. It will attract long-term players such as insurance and pension funds.
What is a Development Finance Institution(DFI)?
- DFI is an agency that finances infrastructure projects of national importance.
- In most cases, these agencies are government-owned. Their borrowings enjoy the government guarantees which help bring down the cost of funding.
- DFI in India: The first DFI in India was the Industrial Financial Corporation of India(IFC) that was launched in 1948. The IDBI, UTI, NABARD, EXIM Bank, SIDBI, NHB were the other major DFIs. Most of them were later converted into banks.
Source: The Hindu
“Shramik Kalyan Portal” of Indian Railways
What is the News?
Indian Railways ensured 100% compliance with the minimum wage pay to contract workers. E-application Shramik Kalyan Portal used for this purpose.
About Shramik Kalyan Portal:
- Launched by: the Indian Railways in the year 2018.
- Purpose: to ensure compliance with the provisions of the Minimum Wages Act. Also, to ensure that contractual workers of Indian Railways get their rightful due.
How does Shramik Kalyan Portal work?
- The portal enables all Railway contractors to register themselves and subsequently add work orders issued by different Railway units.
- The contractors also have to create a profile of each contract worker and update the wages provided to him/her on a regular basis.
- Railway authorities before passing the contractors’ bills have to:
- Check whether contract workers’ wage data have been uploaded by the contractor or not and
- Ensure that wages paid by the contractors conform with the minimum wages fixed by the government.
Source: Indian Express
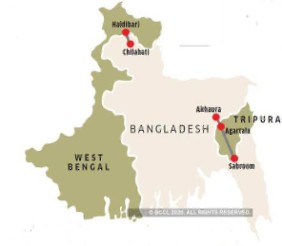
PM to inaugurate “Maitri Setu Bridge”
What is the News?The Prime Minister will inaugurate the ‘Maitri Setu’ bridge between India and Bangladesh.
About Maitri Setu:
- Constructed by: National Highways and Infrastructure Development Corporation Ltd.
- Maitri Setu is a bridge between India and Bangladesh. It is a 1.9 km long bridge over the Feni River. This bridge will connect Sabroom in India with Ramgarh in Bangladesh.
- The name ‘Maitri Setu’ symbolizes growing bilateral relations and friendly ties between India and Bangladesh.
- Significance: With the inauguration of this bridge, Tripura will become the ‘Gateway of North East’. It will have access to Chittagong Port of Bangladesh which is just 80 km from the Sabroom.
About Feni River:
- Feni River is a river in southeastern Bangladesh. It is a trans-boundary river with an ongoing dispute about water rights.
- Origin: The Feni River originates in South Tripura district and flows through Sabroom town and then enters Bangladesh.
Source: TOI
Financial distress in Railways : Reasons and Way Forward
Synopsis: Despite several reforms, Railways is facing financial distress. This article highlights the issues and suggests solutions for financial distress in Railways.Recent developments
- In 2016, the Railway Budget was merged with the General Budget. Earlier, Railways had a separate Budget.
- The Dedicated Freight Corridor will be operational by 2022. It includes
- The Western Dedicated Freight Corridor (WDFC), from Uttar Pradesh to Mumbai
- The Eastern Dedicated Freight Corridor (EDFC), Ludhiana in Punjab to Dankuni in West Bengal.
- Recently the union cabinet approved a proposal to create a single cadre for railways management. This was aimed to eliminate “departmentalism” in railways.
Why Railways is in financial distress?
- First, freight earnings are not improving despite improvement in freight load.
- According to the CEO and Chairman of the Railway Board, the freight loading in January 2021 was the highest ever.
- However, the freight earnings, according to the Revised Estimates for 2020-21 is ₹1,24,184.00 crore. It is lower than what was achieved in 2018-19 (₹1,27,432.72 crore).
- Second, the financial performance index i.e., the Operating Ratio (OR) (the ratio of working expenses to revenues) is not effective. (If the ratio is less than 100%, then Revenues are more than working expenses)
- Currently, the Operating Ratio is less than 100% due to the under-provisioning of the Pension Fund for 2020-21.
- However, the actual Operating Ratio works out to 114.19% and 131.49%, respectively, if the required provision is made for pension payments.
- More worryingly, this is the first time ever, the Indian Railways were unable to adequately provide for the Pension Fund.
What are the future challenges that may increase the financial distress of railways?
- First, traffic revenue is unable to keep pace with the increase in staff costs and pension payments. With the (Eighth) Pay Commission, to be scheduled in 2025-26 the working expenses of railways will further increase.
- For example, the passenger and freight revenues increased by 84.8 % from 2010-11 to 2019-20. While the staff and pension costs almost doubled, by 157%, in the same period.
- This is despite the fact that there is a reduction of about one lakh staff on the roll during this period.
- The increase in the staff and pension costs is mainly due to the implementation of the Central Pay Commission recommendations.
- Second, freight traffic is over-dependent on one commodity, coal. Almost 50% of freight earnings are contributed by the transport of coal.
- With the increasing usage of renewable energy at competitive prices, dependence on coal will reduce. This will affect freight revenues.
- Third, the other major challenge facing the Railways is the burgeoning staff costs including pension. In this scenario, the proposal to recruit an additional 1.5 lakh staff will further increase the financial distress.
Suggestions
- One, increasing the revenues, particularly on the freight front, and a drastic reduction in the number of employees. In this context, the operationalization of two DFCs is significant.
- Two, Railways need to think seriously about life after coal. Adoption of the roll-on roll-off model of transporting loaded trucks on the rail on the DFCs will reduce the overall carbon footprint.
- Three, Corporatisation of the Railways’ Production Units and outsourcing the medical services may reduce work expenses.
- Finally, an annual report called ‘Indian Railways Report’ on the lines of the annual Economic Survey should be placed in Parliament every year. It should detail the physical and financial performance of the Railways. It will make railways more accountable and transparent.
Government released “Rating mechanism for National Highways”
What is the News?
The Ministry of Road Transport & Highways(MoRTH) released the first-ever rating mechanism for National Highways.
About the rating mechanism for National Highways:
- Conducted by: National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) under the Ministry of Road Transport & Highways(MoRTH).
- Objective: The fundamental objective of highway rating is “Minimum time with maximum safety in a stress-free environment” for the highway users. Apart from that, it will also improve the government’s accountability towards road users.
- Parameters: Each toll plaza of the highway is judged based on three major criteria. They are,
- Highway Efficiency(45%): This will consist of an operating speed of traffic, traffic volume, delay at toll plazas among others.
- Highway Safety(35%): This will look at accidents on the highways per year, ambulance response time, road clearance after an accident, etc.
- User Friendly(20%): This will look at the number of footpaths, junctions, adequate structures, etc.
Note: There are no such criteria that have been developed across the world to evaluate the performance of highways from the user perspective.
How many National Highways have been covered in the rating mechanism?
- The rating has been done for all 219 national highway stretches across the country. They cover a distance of 18,668 km.
- Four corridors are selected for rating i.e. Agra-Mumbai(1,084 km), Pune-Vijayawada(856 km), Mumbai-Kolkata(1,927 km), Bangalore-Kanyakumari (655 km).
Best and worst Highway according to the rating mechanism
- The best is the 102-km stretch of the six-lane Ahmedabad-Vadodara section of National Highway (NH)-48.
- The worst stretch is the 45-km Indore-Dewas section of NH-3, which connects Agra to Mumbai.
Golden Quadrilateral:
- The Golden Quadrilateral(GQ) is a national highway network. It is connecting most of the major industrial, agricultural and cultural centres of India.
- It forms a quadrilateral connecting the four major metro cities of India, viz., Delhi (north), Kolkata (east), Mumbai (west) and Chennai (south).
- Managed by: National Highways Authority of India(NHAI) under the Ministry of Road, Transport, and Highways.
- Significance: It is the largest highway project in India and the fifth-longest in the world.
Source: PIB
PM inaugurated ‘Maritime India Summit 2021’
What is the News?
The Prime Minister has inaugurated the Second edition of the”Maritime India Summit 2021′.
About the Maritime India Summit 2021:
- Organised by: Maritime India Summit is being organised by the Ministry of Ports, Shipping & Waterways. The FICCI will act as the Industry Partner in this summit.
- Partner Country: Denmark is the partner country for the Maritime India Summit.
- Objective: To visualise a roadmap for India’s maritime sector for the next decade. Further, the summit will aid India to become the forefront of the global maritime sector.
- Significance: Eminent persons from several countries are attending the summit. There is also potential business opportunities and investments in the maritime domain due to the summit.
Initiatives launched at the Maritime India Summit:
- E-Book of Maritime Vision Policy 2030: It aims to make the Indian maritime industry at par with the top global benchmarks in the next 10 years.
- Sagar-Manthan: Mercantile Marine Domain Awareness Centre (MMDAC): It is an information system for enhancing maritime safety, search and rescue capabilities, security and marine environment protection.
Click Here to Read about Sagarmala Initiative
Source: The Hindu
Prime Minister launches “Mahabahu-Brahmaputra Programme” in Assam
What is the News?
The Prime Minister has launched multiple initiatives in Assam. It includes the Mahabahu-Brahmaputra Programme and the 2 bridges across the Brahmaputra.
Mahabahu-Brahmaputra Programme:
- Aim: It will provide seamless connectivity to the Eastern parts of India. It includes various development activities for the people living around River Brahmaputra and River Barak.
Key Initiatives launched under the Mahabahu-Brahmaputra programme:
- Ro-pax Vessel Services: These are water transport services. It launched between Neemati Ghat (Jorhat) and Majuli island, North Guwahati and South Guwahati as well as Dhubri and Hatsingimari. The benefits of this service include a reduction in travel time, vehicular emission and traffic on the road.
- Inland Water Transport(IWT) Terminal: It will be built at Jogighopa in Assam. The terminal will help in reducing the traffic on the Siliguri Corridor towards Kolkata and Haldia. It will facilitate the uninterrupted movement of cargo to the various North-Eastern States like Meghalaya and Tripura and to Bhutan and Bangladesh as well.
- Launch of E-Portals: E-Portals are launched to promote ease of doing business:
- Car-D (Cargo Data) portal: It will collate cargo and cruise data on a real-time basis.
- PANI (Portal for Asset and Navigation Information): It will act as a one-stop solution for providing information about river navigation and infrastructure.
Dhubri – Phulbari Bridge
- It is a proposed bridge over the Brahmaputra River. It will connect Assam’s Dhubri with Meghalaya’s Phulbari.
- The bridge is planned to be completed by 2026–27. It would be India’s longest bridge over water, which is more than 19 km.
Majuli Bridge:
- The Bridge will connect Jorhat to Majuli (Nemati ghat to Kamlabari ghat). The total length of this bridge is 6.8 Km.
- This bridge will provide connectivity to Majuli Island. This island is the cultural capital and cradle of Assamese civilization for the past 500 years.
Majuli Island:
- It is the world’s largest river island located in the Brahmaputra River, Assam. In 2016, it became the first island to be made a district in India.
- The island is formed by the River Subansiri in the north and River Brahmaputra in the south.
- The island is the nerve centre of neo-Vaishnavite culture. It has many ‘Sattras’ (religious and cultural institutions).
- The tribal communities living on the island include the Misings, the Deoris, and the Sonowal Kacharis.
Source: Indian Express
The issue of Road Safety in India – Explained pointwise
Table of contents:
Recently the World Bank released a report about Road safety in India. The report titled “Traffic Crash Injuries and Disabilities: The Burden on Indian Society”. It measured the number of road accidents happening in India and their various socio-economic impacts. Its findings are important as it highlighted the urgency to focus on road safety in a more comprehensive manner.
Highlights of the World Bank report:
Road accidents in India:
- India was in first place in terms of number of road crash deaths and injuries in the world. India has just 1% of the world’s vehicles but accounts for 11% of all road crash deaths. Further, India is also witnessing 53 road crashes every hour, killing 1 person every 4 minutes.
- India has seen around 4.5 lakh road accidents in the past year. It resulted in at least 1.5 lakh deaths over the past few years.
Socio-Economic Impact of Road accidents in India:
- More loss to poor families: The risk of a victim undergoing disability after a crash is 2 times higher among poor families.
- Accidents result in a decline of 75% of the total household income among low-income groups. Whereas, the decline among high-income groups is only 54%. It underlines poor access to insurance schemes among the less privileged.
- Impact on women: About 40% of women reported a change in their working patterns post-accident. While around 11% reported taking up extra work to deal with the financial crisis.
What are the reasons for the higher number of road accidents and fatality?
The reasons for road accidents in India can be categorized broadly into four categories. (i) human error, (ii) road environment and (iii) vehicular condition (iv) post accidental care-related issues.
1.Human Error: This is one of the biggest factors contributing to accidents on the road. There are many examples of human error. Such as
- Violating traffic rules like jumping signals, overspeeding, etc.
- Driving under the influence of alcohol and other drugs,
- Distractions during driving due to the use of mobile phones
- Driver Fatigue (Not getting enough rest during long-distance travel)
- Not using enough safety devices like Helmets and wearing seat belts
2. Road Environment and design: The reasons for the accident under this category include,
- Presence of many black spots. Black spots are road locations that have a high number of crashes. For example, Sharp corners in a straight road, a hidden junction on the fast road, etc. A survey found out that, these black spots are the prime location for 90% of the road accidents.
- Skewed road traffic engineering: Two-wheelers accounted for the highest share in total road accidents. But their safety was neglected during road traffic engineering and planning. This is evident by the lack of separate lanes for two-wheelers and pedestrians.
- Low-quality infrastructure, standards, and maintenance lead to issues such as potholes, uneven road surfaces, etc.
3. Vehicular condition: Vehicle condition also plays a critical role in accidents. such as,
- Overloading of the vehicle can cause tyre burst. It also increases the chances of rolling over of the vehicles.
- Using old vehicles might lead to more breakdowns and malfunction on roads.
- Weak Vehicle Safety Standards by manufacturers. For example, In 2014, the Global New Car Assessment Programme (NCAP) revealed that some of India’s top-selling car models have failed the frontal impact crash test.
4. Post accidental care-related issues
- Lack of emergency medical services: because of this, the accident victims do not get the first line of medical treatment during the golden hour. Golden Hour refers to the 60-minute time period right after the occurrence of the accident. During which, the chances to prevent death with adequate medical treatment are the highest.
How government is ensuring adequate safety on the roads?
- India signed the and committed to a reduction in fatalities in road accidents.
- Vehicular engineering measures introduced by the government:
- Front and side crash tests for new car models came into force in 2017
- The government introduced the pedestrian protection regulation for new car models. It came into force in October 2018.
- New cars are required to have airbags fitted as standard and to have a speed warning device above 80 km/h.
- A legislative effort by the government:
The government amended the Motor Vehicles (Amendment) Act, in 2019. This is one of the principal Acts used by the government in regulating road safety. The Act provided for- Creating a National Road Safety Board to advise the government on road and traffic management.
- Higher fines for traffic crimes,
- Recalling defective vehicles, dangerous for the environment and people,
- Creating a Solatium Fund for victims of hit-and-run accidents
- Protects Good Samaritans from civil and criminal liability
- Punishment to the owner for violations committed by Juvenile
- Regulated corruption by Automated testing for driver’s licence and fitness certificate (FC)
- Road engineering measures are taken by the government
Suggestions to improve road safety:
- The government has to implement the recommendations suggested in the 3-Year Action Agenda of NITI Aayog. The agenda highlighted important reforms such as
- Standardizing the reporting of accidents
- Create necessary provisions to ensure that the accident victim will reach hospitals within 10 minutes of the accident. This can be achieved by building emergency health services, providing enough ambulances, etc.
- The government can implement the important recommendations of the KS Radhakrishnan panel on Road Safety. The important recommendations were,
- The state governments have to perform a compulsory Audit on road safety to ensure adequate safety standards in the design, construction, and maintenance of roads.
- Creating awareness among people on road safety rules, insurance policies, etc.
- Providing enough compensation to victims on time.
- The government has to implement the Tamil Nadu model of identifying and removing Black spots. Tamil Nadu recorded the highest number of accidents in 2017. But now they have reduced the total number of accidents by 25%.
- Dedicated corridors for vulnerable sections. The government has to provide attention to vulnerable sections like motorists and pedestrians. The government should plan dedicated corridors, especially in places registering higher accidents.
- The Government has to enact the Good Samaritan Laws like Karnataka or Delhi. This will protect the persons involved in helping the accident victims.
- The government has to improve the public transport system and its connectivity. Because an integrated public transport system is safer than motorcycles. Further, it will reduce numerous private vehicles on Indian roads.
- Vehicle manufacturers at present started using the Internet of Things (IoT) enabled connected cars. They can explore further in identifying digital ways on road safety and providing enough safety equipment in vehicles.
A targeted approach and war-footed steps are necessary to ensure road safety in India. Sweden, following the targeted approach, has brought down its road fatalities to five or six annually. India can also create necessary targets to reduce road accidents in India.
What is the “Char Dham Project”?
What is the News?
In the Supreme Court, the government denies any link between the Char Dham road-widening project and the recent flash floods in the Rishi Ganga valley. It claimed many lives and damaged the Tapovan hydro project.
Char Dham Project:
- Char-Dham Road Project is a prestigious two-lane expressway project. The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways is executing this program in Uttarakhand.
- Purpose: The project proposes widening roads up to 10 meters to improve the accessibility to Char-Dham (shrines); Yamunotri, Gangotri, Badrinath, and Kedarnath.
- Implementing Agencies: Uttarakhand State Public Works Department (PWD), Border Roads Organisation (BRO), and the National Highway & Infrastructure Development Corporation Limited (NHIDCL).
- Project Mode: The work under the program is being implemented in Engineering, Procurement, and Construction (EPC) mode.
- Under the EPC model, the project cost is completely borne by the government. But the contractor is legally responsible to complete the project under some fixed predetermined timeline. It may also involve scope for a penalty in case of time overrun.
- Chamba Tunnel: It is a 440-meter-long tunnel built by BRO on the Rishikesh-Dharasu road Highway(NH94) in Uttarakhand. The construction of the tunnel is a part of the Chardham project.
Source: The Hindu
The rising concern of India’s ageing dams
Source: Click here
Syllabus: GS 3 – Infrastructure: Energy, Ports, Roads, Airports, Railways etc.
Synopsis: The ageing dams in India are threatening water security for the future. As the reservoir water is being replaced by soil, technically known as silt or sediment.
Introduction:
- In the race of building large dams, India ranks in the third position in the world.
- India has built over 5,200 large dams. Among which 1,100 large dams have crossed the age of 50 years. Some have even completed over 120 years.
- The number of such dams is going to reach 4,400 by 2050.
What are the issues in water reserviours of India?
After a certain time period, the Silt or sediment start to replace the water in the reservoir due to Siltation. Therefore, the water storage capacity of the dam decreases with time.
Siltation reduces the capacity of Some of India’s Largest dams. Due to Siltation, the functioning of the Bhakra dam has been reduced from 47 years to 88 years.
The medium and minor dams are even in the worst position. They are in such a dangerous position that they can collapse in the near future. This situation is because of their lower shelf life as compared to large dams.
The High siltation rate shows that reservoirs of India are designed with a poor understanding of sedimentation science.
What are the consequences of the siltation of dams for farmers?
- Firstly, it affects crop yield- when soil replaces the water in reservoirs, water availability reduces. It results in less water for the cropped areas. It increases dependency of farmers on rains or groundwater which is already over-exploited. Reduced crop yield results in low Agri credit, crop insurance, and investment.
- Secondly, chances of flooding increases- Due to Low capacity, reservoirs cannot store extra water from rainfall. It will lead to an increase in flooding rates.
For Example, The flooding in Bharuch in 2020, Kerala in 2018 and Chennai in 2015
Way Forward
At present 80% of the India’s large dams are in a situation of becoming obsolete. India need to come together to address the situation urgently. As eventually in 21st century, Nation will not be able to find sufficient water. It will not be able to feed the rising population by 2050, grow abundant crops, create sustainable cities, or ensure growth.
Establishing thought partnerships between the government and private entities
Source – The Hindu
Synopsis: Government should put more effort into establishing more “thought partnerships” with private entities. It is to find appropriate solutions to the policy challenges faced by the country.
Background
- Over the last few years, cooperation between the government and private partners on complex policy issues has increased. For example,
- Induction of private individuals into the civil services through lateral entry scheme.
- Recruitment of private individuals as consultants, officers on special duty by Central government ministries and institutions such as NITI Aayog.
- Such support is critical for tackling issues like; huge vacancies in the central government and over-burdened and under-resourced civil service.
- Moreover, lack of government capacity (knowledge) is evident in suboptimal policy decisions and poor implementation of those policies.
- Hence, there is a strong case for building a “thought partnership” with private entities.
What is a “thought partnership”?
- Thought partnership is different from the recruitment of private consultants.
- Recruitment of private consultants is usually done to support government officials with additional manpower to manage routine tasks.
- In “thought partnership“, private entities will engage with the government in collaborative thinking.
- Thought partnerships are a structured mechanism for private entities. They provide strategic expertise to the government on policy design, evaluation, and implementation.
What are the advantages in building “thought partnership”?
- First, it will help us to utilize the domain knowledge and resources of private individuals. It will ensure the government delivers on its mandate across sectors in the most effective manner.
- For example, take the case of Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY) 3.0.
- Through PMKVY 3.0 the government wants to focus on matching local skilling requirements with local job opportunities.
- However, any plan of this large scale cannot be successful only with the work of a few individuals, a department or even a ministry.
- It requires co-working with different entities, including collaboration between the government and external partners.
- This is where “thought partnership” with private entities becomes helpful.
- Second, the private entities can be used to fund the thought partnership expeditiously without any conditions. For example, Already several domestic and international philanthropies are investing billions of dollars into critical sectors in developing countries including India.
Has India attempted for “systemic thought partnerships” in the past?
Yes, several ministries have attempted systemic thought partnerships occasionally. However, it has not yielded the definitive way forward on government-private collaboration. Some of them are,
- One, the establishment of The National Institute of Public Finance and Policy, Department of Economic Affairs Research Programme.
- It was established after the 2005 Ashok Lahiri Committee report. Report stated that there was not enough knowledge about external capital flows and controls in India.
- The Programme led to the creation of world-class research on capital controls and flows in India, developed by Indian researchers.
- Two, In 2015, the Ministry of Corporate Affairs constituted a research secretariat headed by the Vidhi Centre for Legal Policy.
- It was tasked to support the Companies Law Committee to make informed decisions on the principles involved and international practices in the areas of insolvency, raising of capital, etc.
- Three, Currently the National Institute of Financial Management is working with the Department of Economic Affairs to provide legal research and technical assistance on Indian and foreign financial markets.
- Four, in 2018,the Ministry of Skill Development started engaging with multiple private firms such as Dalberg Global Development Advisors and Samagra-Transforming Governance to conceptualise and design its vision for 2025.
Policy choices made in isolation without proper debate, research, and questioning will produce suboptimal results. It is therefore in the public interest that government should build more “thought Partnership” with private entities to find optimal solutions to the pressing policy challenges faced by the country.
- Over the last few years, cooperation between the government and private partners on complex policy issues has increased. For example,
Hisar Airport Inaugurated Under RCS-UDAN
News: Government has inaugurated the newly constructed Hisar airport in Haryana from Chandigarh under the Regional Connectivity Scheme – Ude Desh Ka Aam Nagrik (RCS-UDAN).
Facts:
- Ude Desh ka Aam Naagrik (UDAN) scheme: It was launched in 2017 by the Ministry of Civil Aviation. The scheme is a component of the National Civil Aviation Policy (NCAP), 2016.
- Aim: To develop a regional aviation market. It seeks to connect under-served and unserved airports in India through the revival of existing airstrips and airports.
- Objectives:
- Create affordable yet economically viable and profitable flights on regional routes.
- Development of remote areas and enhancing trade and commerce and tourism expansion.
- Employment creation in the aviation sector.
- Duration: The scheme would be in operation for a period of 10 years.
- Key Features of the scheme:
- Under the scheme, airlines have to cap airfares for 50% of the total seats at Rs. 2,500 per hour of flight.
- This would be achieved through (1) a financial stimulus in the form of concessions from Central and State governments and airport operators and (2) Viability Gap Funding– A government grant provided to the airlines to bridge the gap between the cost of operations and expected revenue.
- The partner State Governments (other than North Eastern States and Union Territories where contribution will be 10 %) would contribute a 20% share to this fund.
- Regional Connectivity Fund would be created to meet the viability gap funding requirements under the scheme.The RCF levy per departure will be applied to certain domestic flights.
- Phases Under the Scheme:
- UDAN 1.0 and 2.0: During RCS-UDAN version 1.0 & 2.0, 66 airports were identified and 31 heliports (28 unserved heliports and 3 unserved airports).
- UDAN 3.0: During UDAN version 3.0, to increase the tourism potential at the coastal areas, Tourism routes in coordination with the Ministry of Tourism and Seaplanes for connecting Water Aerodromes were included.
- UDAN 4.0: The focus of UDAN 4.0 is on priority areas like North East Region, Hilly States, Jammu and Kashmir, Ladakh and Islands.
Central Vista judgment: Issue of public participation in public projects
Synopsis: The issue of public consultation in the project development process should not be underestimated.
Introduction
In the recent judgment of the Supreme Court, Rajeev Suri v. Delhi Development Authority, Court granted its approval to the proposed redevelopment of the Central Vista in the national capital.
What are the changes proposed?
- In 2009, the Central Vista was considered as a Grade-I heritage precinct after extensive public consultation, which meant that any development inside the area had to be “regulated and controlled” without damaging its impressive style.
- However, the Redevelopment plan includes taking down a number of post-Independence buildings, including the National Museum.
Read more:
Issues in the judgment on central Vista project
Following were 2 issues in the Central Vista Judgment, as per Suhrith Parthasarathy, the advocate of Madras High Court;
- Court refused to acknowledge the existence of a right to public participation, a right, which ought to be seen as fundamental in a democracy.
- Delhi Development Act, 1957 mandated opportunity to the public to place their objections on the record. Although objections were invited from the public, a mere three-days’ notice was given for the hearing on those complaints
- However, majority judgment ruled that the law does not make personal hearings mandatory.
- Issues: 2 issues are involved in this case:
- In the past SC itself held that arbitrary state action violates fundamental rights under article 14 i.e. sufficient time should be accorded to the public if any big change is being introduced to imp. Acts like DDA.
- For Public to scrutinise the project, authentic technical information on the project was available in the public domain.
Issues in general in the public projects
Public participation and architectural services procurement are 2 of several areas that are in urgent need of improvement;
The issue of public Participation
- Horizontal accountability ensures check on government, by creating connected state organizations such as heritage committees and environmental regulators.
- Vertical accountability requires citizen oversight. Citizens are asking for an improved participatory process.
- Government argues that horizontal accountability is in place. Provisions for consultation although are not absent, but the process of consultation is vague.
- Judgment in central Vista is also not clear on the matter of public participation.
- Development of Land Acquisition act provides a few lessons that have spelt out consent required from a minimum number of landowners.
Process of architectural services procurement
- The process of choosing a designer for a public project needs improvement as there is a lack of evaluation criteria and standards for design. Also, weightage is given to lower fees instead of better designs.
- The architecture firms face entry barriers as their expertise is judged on the basis of their company’s turnover. The unreasonable revenue conditions make it difficult for many firms to qualify and also reduce the pool of choice.
Way Forward
- First, according to the dissenting judge, the most basic principles of procedural fairness require the state to make adequate and intelligible disclosures. It becomes more important as the project will have permanent and irreversible consequences.
- Second, for improving consultation, regulations and process have to clearly state what prior disclosures are required, when meetings have to be held and reasons for accepting and declining suggestions should be listed properly.
- Third, the government adopted the Quality and cost based selection (QCBS) for choosing designers. This method specifies requirements for consultants, places higher weightage on their technical capability and lower weightage on financial proposals.
- Fourth, in order to reduce the entry barrier, one can consider the suggestions made by the Architects’ Council of Europe. It suggests dropping turnover requirements and emphasized qualitative selection criteria.
- Weightage given to design value has to be clear and fixed as more than 65% of the registered architects in India are below 35 years and many firms are medium-sized, such changes are all the more required.
Post-Central vista verdict: Need to improve process of developing Public project?
Synopsis: The issue of Central Vista Project has reiterated the need for holistic solutions for the issues in process of the redevelopment projects.
Introduction
The majority ruling decided that the government had followed all processes as required by the regulations and could go ahead with the construction.
However, it is only the one instance, which is visible, the problem of redevelopment project is much bigger. For instance, issues in the Amaravati project as the proposed capital for Andhra Pradesh.
- In this project firstly land was acquired through controversial methods and later on the project was abandoned, creating problems for farmers.
Thus, thoughtful solutions to the issues, is required that can be common for all such projects
What are the areas require improvement?
Public participation and architectural services procurement are the 2 of several areas that are in urgent need of improvement;
The issue of public Participation
- Horizontal accountability ensures check on government, by creating connected state organisations such as heritage committees and environmental regulators.
- Vertical accountability requires citizen oversight. Citizens are asking for improved participatory process.
- Government argues that horizontal accountability is in the place. Provisions for consultation although are not absent, but the process of consultation is vague.
- Judgment in central Vista is also not clear on the matter of public participation.
- Development of Land Acquisition act provides a few lessons that has spelt out consent required from a minimum number of landowners.
Process of architectural services procurement
- Process of choosing a designer for a public project need improvement as there is lack of evaluation criteria and standards for design. Also, weightage is given to lower fee instead of better designs.
- The architecture firms face entry barriers as their expertise is judged on the basis of their company’s turnover. The unreasonable revenue conditions make it difficult for many firms to qualify and also reduce pool of choice.
What regulatory changes can be made?
- First, for improving consultation, regulations and process have to clearly state what prior disclosures are required, when meetings have to be held and reasons for accepting and declining suggestions should be listed properly.
- Second, the government adopted the Quality and cost based selection (QCBS) for choosing designers. This method specifies requirements for consultants, places higher weightage on their technical capability and lower weightage on financial proposals.
- Third, in order to reduce the entry barrier, one can consider the suggestions made by the Architects’ Council of Europe. It suggests dropping turnover requirements and emphasized on qualitative selection criteria.
- Weightage given to design value has to be clear and fixed as more than 65% of the registered architects in India are below 35 years and many firms are medium-sized, such changes are all the more required.
Way forward
- Policymakers maintain that developing countries like India have a quite low state capacity. Therefore, higher standards set in the matured economy and continued by governments with higher capacity cannot be suddenly implanted.
- The dominant argument is that practices will improve as economic growth happens and as the country builds capabilities. However, this incremental approach to be moderated.
PM inaugurates Rewari – Madar section on Western corridor
News: The Prime Minister of India has inaugurated the Rewari – Madar section on Western Corridor.
Facts:
- Rewari – Madar section: It is a part of Western Dedicated Freight Corridor(WDFC).It falls in Haryana (for approximately 79 Km in Mahendragarh & Rewari districts) and Rajasthan (approximately 227 Km in Jaipur, Ajmer, Sikar, Nagaur and Alwar districts) State.
- Significance:
- The section would be beneficial to farmers, industrialists and businessmen in the National Capital Region, Haryana and Rajasthan.
- The ports of Gujarat like Kandla, Pipavav, Mundhra, Dahejetc will have an uninterrupted connectivity to the Northern parts of India.
- With the dedication to the Nation of the 351-km Bhaupur-Khurja section, and construction of connecting link between Khurja – Boraki-Dadri- Rewari, seamless movement between WDFC & EDFC can ensue.
Additional Facts:
- Dedicated freight corridor(DFC): It is meant to create a safe and efficient freight transportation system in the country.
- Nodal Body: Dedicated Freight Corridor Corporation of India(DFCCIL) is constructing the Western DFC (1506 Route km) and Eastern DFC (1875 route km including Sonnagar-Dankuni PPP Section).
- EDFC: The EDFC is starting from Sahnewal near Ludhiana (Punjab) and will pass through the states of Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar and Jharkhand to terminate at Dankuni in West Bengal. It is being majorly funded by the World Bank.
- WDFC: The Western Corridor is connecting Dadri in Uttar Pradesh to Jawaharlal Nehru Port (JNPT) in Mumbai and will traverse through the states of UP, Haryana, Rajasthan, Gujarat and Maharashtra of WDFC. Approx. 40% of WDFC is in Rajasthan. It is being majorly funded by Japan International Cooperation Agency(JICA).
Click here to read more about Dedicated Freight Corridor
Government launches Indian Railways Freight Business Development Portal
News: The Ministry of Railways has launched Freight Business Development Portal.
Facts:
- Freight Business Development Portal: It is an exclusive portal to promote and develop the railways freight business.
- Key Features:
- It ensures that all operations stay customer centric, reduce the costs for logistics providers, provide online tracking facilities for suppliers and also simplify the process of goods transportation.
- It aims to replace physical processes with online ones to minimize the need of human to human interaction.
- The portal has a focus on ease of doing business and to bring more transparency and to provide professional support.
Need for the Portal:
- Indian Railways is the backbone of the country’s logistics sector the portal will improve the logistics capacity of the Railways to the next level.
- Indian Railways embraced a “Freight on Priority” policy to push for aggressive customer-centric approach. The portal will expand the policy further.
Supreme Court Judgment on Central Vista Redevelopment Project
Supreme Court pronounced 2-1 judgment and cleared the Central Vista Redevelopment Project.
Petition challenging the Centre’s change-of-land-use notification of March 2020 for 86 acres of land was filed in SC.
Following statements were put forward by the majority judgment and dissenting judge:
More about judgment
SC Court in its judgment held that it found no issues in the following orders and found them as per laws and procedures.
- “No Objection” by the Central Vista Committee (CVC);
- “Approval” by the Delhi Urban Art Commission (DUAC) as per the DUAC Act, 1973;
- “Prior approval” by the Heritage Conservation Committee (HCC) under Building Byelaws for Delhi, 2016.”
- Exercise of power by central government under DDA (Delhi Development Authority) Act, 1957.
- Environmental Clearance (EC) recommendation for the project by the Expert Appraisal Committee (EAC).
SC in its judgment also made a statement regarding the limits on its powers. As per the bench, development policies of the Government of the day must be debated in the Parliament. The role of the Court is limited to examining their constitutionality and not to govern.
Further, it asks for the creation of smog towns and deployment of smog guns to mitigate the pollution from construction materials and directs that waste management at the site be subjected to constant monitoring.
What were the issues raised in the petition challenging Central Vista Project?
Supreme Court was hearing the petition on the following main grounds, put forward by the petitioner:
- Change of land use: DDA in its notification made changes in the land use to facilitate the use of public open spaces such as a district park and children’s play area for the use of government office.
- Violations of municipal law: consultation with Delhi Urban Commission (DUAC) had to be completed at the plan conception stage itself.
- In the absence of a comprehensive consultation, the approvals were granted without proper application of mind.
- Violations of environmental law: Parliament building was granted environmental clearance from the Ministry of Environment, Forests & Climate Change without any Environment Impact Assessment (EIA).
- Change in heritage Status: Heritage Conservation Committee allowed the demolition of post-independence constructions by redefining the ‘Heritage status’.
- Central Vista Committee(CVC): As per the petitioner, CVC was set up to rush the approvals and it consists of the members, who were proponents of the central vista project. Thus, there is an apparent conflict of interest.
For more Info. on Issues: Issues with Central Vista Project
What is Central Vista and Central Vista Redevelopment Project?
History of Central Vista development
- Britain’s King George V on December 12, 1911, at his coronation announced the transfer of the seat of the Government of India from Calcutta to the ancient Capital of Delhi.
- This 20 years-long project of Central Vista development was led by architects Edwin Lutyens and Herbert Baker. It was completed in 1927 and inaugurated by Viceroy Lord Irwin.
- Central Vista is 3.2 kilometre area in Delhi housing Parliament House, Rashtrapati Bhavan, North and South Blocks, Rajpath, India Gate, National Archives and the then princes’ houses around India Gate.
- In the 1962 Master plan of Delhi, site was declared a heritage precinct as an “important site to meet the aspirations of a rich culture”.
About the Central Vista Redevelopment Project
- Project was announced by Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs in 2019 as a redevelopment project to give a new identity to the ‘power corridor’ of India.
- Redevelopment project includes
- Construction of a new parliament next to existing one,
- Prime minister and vice-president’s residences along with 10 building blocks that will accommodate all government ministries and departments.
- Revamping of the 3-km-long Rajpath — from Rashtrapati Bhavan to India Gate.
- Project will change the structure of the 86-acre area in Lutyens’ Delhi that shows off India’s iconic buildings such as South and North blocks of Central Secretariat, Parliament House, and Rashtrapati Bhavan.
Read Also :upsc syllabus
Parliament Complex
- Complete project is estimated to cost around Rs. 20,000 crores. Of this amount, around Rs. 1000 crores is allocated for construction of Parliament Building.
- It will be a triangular-shaped Parliament building and spans across over 64,500 square metres.
- It will be able to accommodate 336 more Lok sabha members and 139 more Rajya Sabha members than the current capacity i.e. 888 Lok Sabha members and 384 Rajya Sabha members.
- Building is projected to complete by 2022, for which Tata Projects won at Rs. 861.90 crores.
Why the Central Vista redevelopment Project has been planned?
- Firstly, the Current Parliament was built in 1927 to house the legislative council and was not intended to house a bicameral legislature that the country has today. The current building will be under more stress when the number of seats to Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha are raised.
- Secondly, the present Parliament House signifies an imperial origin, whereas India is a successful citizen-led democracy. Thus, the present parliamentary building is not in accordance with the aspirations of independent Indian citizens and the new building will stand out as an institution created by 130 crore citizens.
- Thirdly, there are international examples of building new parliamentary structures after gaining independence.
- The Capitol Building in the USA was constructed within 25 years of the country’s independence.
- In Brazil, the National Congress Building was constructed, almost 70 years after Independence, in 1960.
- Fourthly, Present Parliamentary complex was built by the British on their own patterns and designs. New building’s design and interiors will capture Indian values and the rich diversity of our regional arts, crafts, textiles, architecture, and culture.
- Fifthly, World history proves that Public infrastructure projects playing a key role in reviving economies in distress. For ex; the Tokyo Tower in Japan, built after World War II, provided employment to thousands of workers, instilled a greater sense of nationalism, and contributed to the resurgence of the Japanese economy.
- Sixthly, the existing building does not conform to fire safety norms and is not earth quake proof. Water and sewer lines are also haphazard and this is damaging its heritage nature. 2001 Parliament attack is a fit example questioning the safety.
Although SC has given a green light to Central Vista Project, it also underlined the need for the significance of transparency i.e. if the relevant information is not placed in the public domain, public will be ill-equipped to understand the need and rationale behind such projects.
Government should become more transparent and try to bring in a consultation process at the initial stage of the project developments to maintain a level of confidence among people of the country.
Government kicking off Seaplane Services on selected Routes
News: Union Ministry of Ports, Shipping, and Waterways has announced that it has kickstarted the process of commencing operations of the Seaplane services on select routes.
Facts:
- What is Seaplane? Seaplanes are typically fixed-wing aircraft with a much fewer number of seats and can take off from and land on water.
- How will it work? Sea Planes will utilize the nearby water bodies for take-off and landing and thus connect those places in a much economical way as conventional airport infrastructure like a runway and terminal buildings are not required for seaplane operations.
- Implementation: The services will be under a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) framework through potential airline operators and will be executed and implemented through Sagarmala Development Company Ltd (SDCL), which is under the administrative control of the Ministry.
- Proposed Locations for Seaplane Services: The proposed Seaplane Services under Hub and Spoke model include islands of Andaman & Nicobar and Lakshadweep, Guwahati Riverfront & Umranso Reservoir in Assam, Yamuna Riverfront / Delhi (as Hub) to Ayodhaya, Srinagar (Uttrakhand), Chandigarh and many other tourist places of Punjab & HP; Mumbai (as Hub) to Shirdi among others.
- Is there any operation Seaplane Service? One Seaplane Service which is already in operation between Kevadia and Sabarmati Riverfront in Ahmedabad which was inaugurated by the Prime Minister in October 2020.
- Significance:
- Seaplane Service will provide air connectivity to various remote religious/tourist places.
- It will save travel time and stimulate localized short distance travelling especially in the hilly regions or across the rivers/lakes as well as boost tourism and business activities.
- It will generate employment opportunities and stimulate tourism in these new locations, which will consequently contribute to the country’s GDP in the long run.
Read more:-Daily current affairs
Cabinet approves 3 infra projects
Source: The Hindu
News: Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs(CCEA) has approved three key infrastructure proposals.
Facts:
What are the three key infrastructure projects approved? The three projects proposed by the Department of Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade(DPIIT) are:
- Krishnapatnam Industrial Area in Andhra Pradesh
- Tumakuru (Tumkur) Industrial Area in Karnataka and
- Multi-modal logistics hub (MMLH) and multi-modal transport hub (MMTH) at Greater Noida in Uttar Pradesh.
Read Also : Current affairs for upsc
Additional Facts:
- Industrial Corridor Programme: The objective of the Programme is the creation of greenfield industrial cities with sustainable, ‘plug n play’, ICT enabled utilities to facilitate the manufacturing investments into the country.
- Krishnapatnam Industrial Area and Tumkur Industrial Area are part of Chennai Bengaluru Industrial Corridor(CBIC) project.
- These corridors will help in attracting investments into manufacturing and positioning India as a strong player in the Global Value Chain.
- Multi Modal Logistics Hub(MMLH) & Multi Modal Transport Hub (MMTH): The logistics hub at Greater Noida, UP will be developed as a world-class facility that will provide efficient storage/transitioning of goods to/from the Dedicated Freight Corridors(DFC) and offer a one-stop destination to freight companies and customers.
- The facility will not only provide standard container handling activities but also provide various value-added services to reduce logistics cost with improved efficiency of operations.
Why Dedicated Freight Corridor matters — for Railways, the country?
Source: The Indian Express
News: Prime Minister has inaugurated a 351-km section between Khurja and Bhaupur in Uttar Pradesh for commercial operations as a part of Eastern Dedicated Freight Corridor(EDFC).
Facts:
- Dedicated Freight Corridors(DFC): These are freight-only railway lines to move goods between industrial heartlands in the North and ports on the Eastern and Western coasts.
- The DFC consists of two arms.
- Eastern DFC: It is a 1,839-km line that starts from Sahnewal (Ludhiana) in Punjab and ends at Dankuni in West Bengal.It is being majorly funded by the World Bank.
- Western DFC: It is around 1,500-km line that starts from Dadri in Uttar Pradesh to JNPT in Mumbai, touching all major ports along the way.It is being majorly funded by Japan International Cooperation Agency.
- Dedicated Freight Corridor Corporation of India Limited(DFCCIL): It is a Public Sector Undertaking(PSU) corporation run by the Ministry of Railways to undertake planning, development, and mobilisation of financial resources and construction, maintenance and operation of the Dedicated Freight Corridors(DFC).
- Benefits of DFCs:
- These freight corridors will help reduce the cost and allow faster transportation.
- Around 70% of the freight trains currently running on the Indian Railway network are slated to shift to the freight corridors, leaving the paths open for more passenger trains.
- Tracks on DFC are designed to carry heavier loads than most of Indian Railways.DFC will get track access charge from the parent Indian Railways and will also generate its own freight business.
- The DFCs will allow much shorter transit times from freight source to destination which means it will reduce the time by up to 50% in some cases.
World Bank Signs $500 Million Project to Develop Green, Resilient and Safe Highways in India
What is commission for air quality management
Source: PIB
News: The Government of India and the World Bank has signed a $500 million Green National Highways Corridors Project.
Facts:
- Objective: To demonstrate safe and green National Highway corridors in selected States and enhance the institutional capacity of the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways in mainstreaming safety and green technologies.
- States covered under the project: Rajasthan, Himachal Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh and Andhra Pradesh.
- Key Features of the Green National Highways Corridor Project:
- The project supports an in-depth analysis of gender-related issues in the transport sector along with help in creating jobs for women by training women-led micro enterprises and women collectives to implement green technologies in the highway corridors.
- The project will also strengthen and widen existing structures; construct new pavements, drainage facilities and bypasses; improve junctions and introduce road safety features
Steps needed to make spectrum Auction successful
Context: Government should take lessons from 2016 spectrum auction failure and take steps to get the present auction right.
Discuss the parameters on the auction of radio spectrum.
- A new round of auction has been cleared by government to be held using the methodology of Simultaneous Multiple Round Ascending (SMRA) after 4 years.
- The Telecom Regulatory Authority of India recommended the auction spectrum in the sub-GHz bands of 700, 800 and 900 MHz along with mid-band frequencies in bands of 1800, 2100, 2300, and 2500 MHz across the 22 Licensed Service Areas (LSAs) of the country.
- The total spectrum to be auctioned is about 2,251 MHz. The potential revenue growth to the government at reserve prices is about $50 billion. Total reserve price of spectrum put on auction in 2016 was about $90 billion.
What are the factors that determine the success of spectrum auction?
- Firstly, the reserve price. Cross country spectrum database shows that the reserve price is positively correlated to the winning bid price. However, a higher reserve price also stops bidders from bidding for more spectrum blocks, resulting in lower amounts of spectrum sold as happened in 2016.
- Secondly, Factor of VoIP subscribers. Over The Top (OTT) providers are providing substitute goods such as Voice Over Internet Protocol (VoIP) and are capturing a greater mind share of customers while remaining somewhat invisible to government regulators.
- The scraping away of the position of telcos in front of OTTs would impact their relationship in the overall digital value network of devices, connectivity and apps, that could result in a lower willingness to pay.
- Third, allocation of unlicensed spectrum for Wi-Fi. Wi-Fi shared the load of carrier network and reduces the demand for mobile network capacity. If government want to expand the Wi-Fi facilities, it needs to keep more spectrum unlicensed. The more the unlicensed spectrum allocation, the lower will be the demand for licensed spectrum.
- Fourth, visibility of spectrum that will be up for auction. The amount of spectrum for 5G auction (namely 3.4-3.6 GHz) that will be made available by the government in late 2021 is not clear. It is creating a confusion among companies, should they acquire the spectrum now, or wait for subsequent auctions.
- Fifth, reserve prices of different bands for the forthcoming auction as recommended by TRAI indicate that the average price per MHz per population (a common metric used for comparing spectrum prices) is around $3 for sub-GHz band and $1.70 for mid-band.
What are the key steps to get the auction right?
As Spectrum is a perishable scarce resource and lose its value if left unused, it is important for the government to ensure that the spectrum put on the block is sold successfully, unlike 2016. Therefore, following steps are recommended before the auction begins:
- First, Government should recheck reserve prices and consider reducing it further, especially of the “golden band” or 700 MHz band, which is important for covering the surrounding areas of the country.
- Secondly, Government should release more unlicensed spectrum in 2.4/5/60 GHz for multiplying Wi-Fi as a suitable supplement to the carrier network. This will increase the placements of the Public Wi-Fi project which got the approval of cabinet recently.
- Thirdly government should provide clarity about future auctions, especially the major chunks of spectrum that can be put on the block in 3.3/3.6/26/28 GHz.
- Lastly, government should release guidelines on how they will regulate the auctions and what will be regulated so that the telcos and OTTs can join hands to provide superior and better services for the benefit of the consumers.
Indian Railways issues draft National Rail Plan
Source: Click here
News: Indian Railways has issued a Draft National Rail Plan.The plan will be a common platform for all future infrastructural, business and financial planning of the Railways.
Facts:
Key objectives of the Plan:
- Create Demand: To create capacity ahead of demand by 2030, which in turn would cater to growth in demand right up to 2050 and also increase the modal share of Railways from 27% currently to 45% in freight by 2030 as part of a national commitment to reduce net zero carbon emission by 2030.
- Forecast growth of traffic in both freight and passenger year on year up to 2030 and on a decadal basis up to 2050.
- Formulate strategies based on both operational capacities and commercial policy initiatives to increase modal share of the Railways in freight to 45% by 2030.
- Reduce transit time of freight substantially by increasing average speed of freight trains from present 22 Kmph to 50 Kmph.
- Reduce overall cost of Rail transportation by nearly 30% and pass on the benefits to the customers.
- Map the growth in demand on the Indian Railway route map and simulate the capacity behaviour of the network in future.
- Identify infrastructural bottlenecks that would arise in future with growth in demand.Select projects along with appropriate technology in both track work, signalling and rolling stock to mitigate these bottlenecks well in advance.
India and Bangladesh PM jointly inaugurates Chilahati-Haldibari rail link
Source: Click here
News: India and Bangladesh Prime Minister has jointly inaugurated a railway link between Haldibari in India and Chilahati in Bangladesh during the virtual bilateral summit.
Facts:
- Haldibari-Chilahati rail link: This rail link was part of the Broad Gauge main route from Kolkata to Siliguri.However, the war of 1965 effectively cut off all the railway links.
- Significance: This rail link is expected to enhance the connectivity to Assam and West Bengal from Bangladesh.
- Other rail which are operational? The other rail links which are operational between India and Bangladesh are — Petrapole (India) – Benapole (Bangladesh); Gede (India) – Darshana (Bangladesh); Singhabad (India)-Rohanpur (Bangladesh); and Radhikapur (India)–Birol (Bangladesh).
PM-WANI: Revolutionise the way India accesses the internet
Context: PM-WANI has the potential to revolutionise the way India accesses the internet.
What are the key features of Pradhan Mantri Wireless Access Network Interface (PM-WANI)?
- Bring large scale deployment of Wi-Fi hotspots through the country to drive up connectivity options and improve digital access.
- The scheme envisages setting up of public Wi-Fi networks and access points by local Kirana and neighbourhood shops through public data offices (PDO will be set up on the lines of Public Call Offices (PCOs)) that will not involve any licence, fee or registration.
What are the needs of PM-WANI?
- To create value for the consumer.
- To quickly reach countrymen in the remotest areas.
- India’s tele-density of landlines never exceeded 7 per 100 people but due to mobile it exceeded to 90 per 100 people.
- India grew from 302 million internet subscribers to 750 million.
- India is one of the fastest growing internet markets in the world.
- To deliver a resilient and reliable connection to every Indian and reliable access everywhere.
- Despite excellent advances in 4G technology, wired connections still offer superior quality, reliability and throughput.
How PM-Wani can revolutionise access to internet?
- UPI created common payments infrastructure that unbundled whose app you use to pay from which bank your money was in.
- This resulted in 3 Cs — greater convenience, higher confidence and lower costs.
- PM-WANI unbundles whose wired connection you use from who you pay to use that connection.
- It allows them to interoperate and focus on connecting the last user. It is built on unbundling three as — access, authorisation and accounting.
What are the dimensions along which PM-WANI has broken away from the past?
- PM-WANI has liberalised the resale of bandwidth. Earlier only licensed players could become Internet Service Providers and resell bandwidth.
- This has led to the top 5 ISPs owning 75 per cent of the volume of all wired subscribers.
- PM-WANI allows anyone — a kirana shop owner, a tea-stall vendor, or a Common Service Centre to resell internet to its customers without a licence and without fees.
- By installing a wireless router, they can get on the PM-WANI network and start selling connectivity.
- These small vendors will be called Public Data Offices (PDOs), in a deliberate hark back to the Public Call Offices of yore.
- Due to this deregulation, the distribution of endpoints of PM-WANI will be selected by entrepreneurs rather than being decided top-down.
How PM-WANI is forward-looking in its design?
- Presence of robust identity infrastructure in the form of Aadhaar and DigiLocker. It will help to authenticate its users.
- This architecture also allows a central data balance and central KYC, that users can use inter-operably across all PDOs.
- The network operators then settle accounting between them, much like how telecom operators settle call termination charges.
- Indians can log in once and enjoy access on all available WiFi networks.
- It also allows international travellers to take advantage of India’s connectivity, without paying exorbitant roaming charges to their home networks.
Union Minister inaugurates Koilwar Bridge
Source: Click here
News: Union Minister for Road Transport and Highways has inaugurated the three-lane Koilwar bridge.
Facts:
- Koilwar Bridge: It is a bridge constructed over the Sone river in Bihar. This rail-cum-road bridge connects Arrah with Patna, the capital of Bihar state in India.
Additional Facts:
- Son River: It is the second largest of the Ganges southern tributaries after Yamuna River.Its chief tributaries are the Rihand, Kanhar and the North Koel.
Draft Indian Ports Bill, 2020
Initial status: Ministry had circulated the draft Indian Ports Bill 2020 for inputs from stakeholders. Feedback incorporated in the draft Indian Ports Bill, 2021
Present status: Draft Indian Ports Bill, 2021 is under consultative stage.
About Draft Indian Ports Bill, 2020
Ministry: Ports, Shipping and Waterways
Aim:
- To enable the structured growth and sustainable development of ports to attract investments in the Port sector for optimum utilisation of the Indian Coastline by effective administration and management of ports.
- The Bill will repeal and replace the Indian Ports Act, 1908.
Key Provisions of the Bill:
- Constitution of Maritime Port Regulatory Authority
- Formulation of the National Port policy and National Port plan in consultation with Coastal State Governments, State Maritime Boards and other stakeholders.
- Formulation of specialised Adjudicatory Tribunals namely Maritime Ports Tribunal and Maritime Ports Appellate Tribunal to curb anti-competitive practises in the port sector and act as a speedy and affordable grievance redressal mechanism.
Way Forward
- The Bill seeks to provide increased opportunities for public and private investments in the Indian maritime and ports sector by way of removing barriers to entry, simplifying processes and establishment of agencies and bodies to plan and enable growth of the ports sector.
- Enhancing “Ease of Doing Business’,it will provide greater impetus to a self-reliant domestic investment climate in the maritime sector, towards Atamanirbhar Bharat initiatives of the Government.
Central Vista Project: What are the benefits and issues associated to it?
Amid the controversies surrounding the Central Vista Project, the PM of India laid the foundation stone of the new Parliament building. Objections were raised against the project due to the land-use changes and environmental clearances issue to the project by authorities. The matter is being heard by the Supreme Court.
In its recent order, the Supreme Court barred the government from any further activities related to the Central Vista Project and reserved the judgment. In its judgment, SC stated no construction, demolition, or chopping of trees should take place at the Central Vista project. However, SC allowed the government to lay the foundation stone of the project and carry on paperwork.
About Central Vista Project
The present Parliament building was inaugurated in 1927. It was having three halls, the Chamber of Princes, State Council, and Central Legislative Assembly, known as Library Hall, Rajya Sabha, and Lok Sabha respectively in the post-Independence era. Two floors were added in 1956 to accommodate the enhanced requirements.
Central Vista project includes the construction of triangular Parliament building, common Central Secretariat and revamping of the 3-km-long vista or Rajpath — from Rashtrapati Bhavan to India Gate.
Features of New Parliamentary building
- New Parliament Building Complex, will be of triangular shape, spreading over 64,500 square meters with the capacity of housing 1,224 Members of Parliament. By 2024, there will be a chamber for every MP.
- It will have a grand Constitution Hall showcasing an original copy of the Constitution.
- The Central Vista project has a work completion deadline of 2024 and the new Parliament building complex is expected to be complete by 2022 to commemorate 75 years of India’s Independence.
- The building will be energy efficient and accessible to all.
- The Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha Halls will have high-quality acoustics and audio-visual facilities, improved and comfortable seating arrangements, effective and inclusive emergency evacuation provisions, with high-level security for the members.
- There will be Seamless access between the current and new Parliament buildings, the Chamber for Members, the Parliament Annexe, and Library buildings will form a legislative enclave, which will stand as an iconic and modern colosseum of democracy.
What are the issues raised against Central Vista Project?
Notification for the project was issued in April and cleared by the environment ministry’s Expert Appraisal Committee immediately when the country was suffering from COVID Pandemic. Critics called the project ill-timed with several loopholes in the approval process were pointed out.
Lack of transparency
- As per the reports, planning for the project is ongoing since 2015, but behind the curtains. There is no information about the tender issued or either the process followed, or the criteria for selection of companies building it. There was no exhibition of the proposed buildings was held, no data revealed, no models or drawings displayed.
Changes in heritage status
- Central Vista has been accorded the highest Grade 1 heritage status by the Unified Building Bye-Laws of Delhi. Grade 1 classified buildings cannot be changed, and “no intervention can be made unless it is in the interest of strengthening and prolonging the life of the buildings”.
- However, later on, Heritage Conservation Committee made a distinction between pre-Independence and post-Independence buildings to redefine the status of ‘heritage’, allowing the demolition of post-independence constructions, built by Indian architects and engineers in the 60s.
- It effectively, allowed the demolition and replacement of buildings like Krishi Bhawan, Udyog Bhawan and Rail Bhavan, in addition to the National Museum and the Indira Gandhi National Centre for the Arts (IGNCA).
Land Use Changes
- In 2020 Delhi Development Authority made changes in the land use to facilitate the use of public open spaces such as a district park and children’s play area be changed for use as government offices.
- Before notification, there was a 60/40 split between public/ semi-public (60 per cent) use including museums, galleries, centres of arts, national library, (the Delhi) high court, etc., and government use (40 percent).
- After notification, it was changed to 95 percent for government use and 5 Percent for public and semi-public use.
Environment clearance
- On April 22, the new Parliament building was granted environmental clearance from the Ministry of Environment, Forests & Climate Change without any Environment Impact Assessment (EIA).
Cases filed
- Rajeev Suri vs. the Union of India —was filed in the Delhi High Court in March 2020 against this land-use change and another petition was filed regarding violations of the heritage status of Central Vista.
- The petitions were transferred to the Supreme Court and are now in the apex court’s domain.
Why new Parliament complex is required?
- Firstly, the Current Parliament was built in 1927 to house the legislative council and was not intended to house a bicameral legislature that the country has today. The current building will be under more stress when the number of seats to Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha are raised.
- Secondly, the present Parliament House signifies an imperial origin, whereas India is a successful citizen-led democracy. Thus, the present parliamentary building is not in accordance with the aspirations of independent Indian citizens and the new building will stand out as an institution created by 130 crore citizens.
- Thirdly, there are international examples of building new parliamentary structures after gaining independence.
- The Capitol Building in the USA was constructed within 25 years of the country’s independence.
- In Brazil, the National Congress Building was constructed, almost 70 years after Independence, in 1960.
- Fourthly, Present Parliamentary complex was built by the British on their own patterns and designs. New building’s design and interiors will capture Indian values and the rich diversity of our regional arts, crafts, textiles, architecture, and culture.
- Fifthly, World history proves that Public infrastructure projects playing a key role in reviving economies in distress. For ex; the Tokyo Tower in Japan, built after World War II, provided employment to thousands of workers, instilled a greater sense of nationalism, and contributed to the resurgence of the Japanese economy.
- Sixthly, existing building does not conform to fire safety norms and is not earth quake proof. Water and sewer lines are also haphazard and this is damaging its heritage nature. 2001 Parliament attack is a fit example questioning the safety.
Conclusion
Central Vista Project should be presented as the project fulfilling the aspirations of people, not something imposed on the people. All the valid concerns should be taken into account and proper assessment should be carried out to ascertain that the project will not have any negative impact.
Andhra Pradesh’s three capital plan
Context –Impact of Andhra Pradesh decentralization and inclusive development of all regions bill, 2020.
What is Andhra Pradesh Decentralization and Inclusive Development of All Regions Bill, 2020?
It is an act of Andhra Pradesh Legislature containing provisions relating to the decentralization of governance in the state of Andhra Pradesh so that establishments for additional two capitals can be made at any place outside Amaravati.
This law paves the way for three capitals for the state.
- Amaravati– legislative capital.
- Visakhapatnam– executive capital.
- Kurnool– judicial capital.
The proposed three-capital plan claims to achieve the following-
- Equal development of different regions– The state government claims that it would allow an even development of the state. It would ensure justice to everyone and every region.
- Decentralization- It also claims it’s a good idea to decentralize power across the state as there have been several imbalances among the regions which had often led to agitations. Three capitals will lead to equitable development.
- Growth perspective– Furthermore, it would be a boost to urbanization and then economic development. In India, cities contribute anywhere between 59% and 70% of the GDP.
Why implementing this idea will be difficult?
- Coordination and logistics fear: Coordinating between seats of legislature and executive in separate cities will be easier said than done, and with the government offering no specifics of a plan, officers and common people alike fear a logistics nightmare.
- Hamper administrative efficiency – Executive capital Visakhapatnam is 700 km from judicial capital Kurnool, and 400 km from legislative capital Amaravati. The Amaravati-Kurnool distance is 370 km. The time and costs of travel will be significant.
- Infrastructure requirements: It will need constructing new buildings in the new capitals.
- Environmental impact- Unrestrained real estate interests can co-opt local State institutions and sabotage environmental interests.
- Impact on farmers– the Andhra government had acquired around 30 thousand acres of land approximately from the farmers in and around the Amaravati region. So the decision of changing the capital may affect most of the farmers living out there.
Way forward-
- The success of distributed development depends on a well-developed infrastructural network linking the growth centres.
- The ongoing processes of preparing the Master Plan and Strategic Plan for the Visakhapatnam Metropolitan Region are an opportunity to address environmental challenges.
- The bill is thin in details but offers hope in its broad contours of pursuing inclusive development through Zonal Planning and Development Boards.
7 PM Editorial |New Economic Realities and Need of Decentralization|6th August 2020
Infra Investment
Context: Ministry of statistics and programme implementation (MOSPI) has released its latest report incomplete infrastructure projects.
What were the problems highlighted in the MOSPI report?
- Inadequate data: The latest report showed that of a current total of 1,661 incomplete infrastructure projects, each costing above ₹150 crore, delays were assessable only for 754 projects on which timing data were available.
- 70% were delayed (539 projects), with an average delay of three-and-a-half years.
- Stated reasons for delay: Reasons include land acquisition and green clearance.
- Projects are expected to stimulate both supply and demand through wages paid to construction labour.
- Delayed payments: Payments by governments (both Centre and states) to vendors of all types, not just construction contractors, are delayed. It is commonly estimated that these dues amount to ₹2 trillion at a minimum.
- Domino effect: Fiscal failure to pay on time has a domino effect on the financial sector. The unpaid vendor has to borrow more to cover enhanced working capital requirements.
- For instance, the default of Infrastructure Leasing and Financial Services (ILFS) in September 2018, when the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) had to move quickly to prevent a financial meltdown.
- Poor reporting: The MOSPI report mentions the repeated failure of projects to report milestones, which would have helped reveal the true cause of delay.
- Overall effect:
- The medium-term fiscal plan required under the Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM) legislation has become a mere statement where the fiscal shortage is not the true left over.
- Governments take on more expenditure commitments for future years than they know can be put up within the fiscal deficit path committed to. If payment dues exceed, they are simply delayed.
- Many infrastructure companies are unwilling to engage with governments because of payment delays.
What are the steps to be taken?
- The fiscal system is deeply in need of reform, towards multi-year budgeting of committed expenditures, and calculation of deficits as a serious remaining rather than as a priority in itself to which expenditures will be shaped.
- Former RBI governor Raghuram Rajan has warned that without “relief” payments the potential growth rate of the economy would be seriously reduced. Hence relief payments are required.
Way forward
- Nothing would raise the potential growth rate of the Indian economy as much as a one-time payment of all past dues, and a credible commitment to future payments on time.
- The Centre should give interest-free loans to states with bullet payment after 50 years. The funds “are to be used for new or ongoing capital projects needing funds and / or settling contractors’/ suppliers’ bills on such projects”.
Air India Strategic Sale
Context: Recently, the Government of India announced few changes to facilitate the sale of Air India.
Background
- As part of the strategic disinvestment, the government initiated for the complete disinvestment process of debt burdened Air India.
- Before the start of the current financial year, Air India had more than Rs 60,000 crore as debt and with the coming of the pandemic, debt burden is getting accumulated.
- Due to increasing debt burden, the Government has been pushing for the strategic sale of Air India.
- Following the failure to receive a single bid in the first attempt the government has initiated the disinvestment process of Air India for the second time.
What are the new changes?
- Earlier, the government had mandated a fixed level of debt i.e. 23,286.50 crore to be taken by buyers along with the sale.
- The government, through its recent announcement will now allow the prospective bidders the flexibility to decide the level of debt they wish to take on while buying the airline.
- Second, the winning bidder will have to deposit at least 15 per cent of the bid amount in cash with the government ahead of the share transfer.
- Also, the government has extended the deadline from October 30 to December 14 to allow potential bidders to carefully evaluate the new terms and conditions.
Whether the latest changes would be enough to attract the buyers?
- Lack of buyers: Most best bidders who are affected by the pandemic are now struggling to survive themselves.
- Unattractive Aviation sector: Estimates suggest that most airlines will struggle to be financially viable even in 2021 fearing the second wave of COVID infections.
Redesign policy for private investment
Source- The Indian Express
Syllabus – GS 3- Investment models.
Context- Partnerships with various stakeholders in the private sector is required for sustainable infrastructure creation in India
What is PPP investment model?
Public Private Partnership is a cooperative arrangement between public and private sectors. The PPP model displays three essential characteristics:
- Long term contractual arrangement.
- A significant level of responsibility and risk that is transferred from public to private sector.
- Contractual arrangements are built around performance based outcomes.
What are the challenges on ramping up private investments in infrastructure?
- Policy reforms– Refreshing institutions and policies for channeling financing.
- Stable ecosystem– Providing a stable, durable, and empowering ecosystem for private players to partner with government entities in the task of infrastructure-creation.
What are the recommendations of Vijay Kelkar Committee on Revisiting and Revitalizing PPP Model?
Vijay Kelkar Committee Finance Minister in the Union Budget 2015-16 announced that the PPP mode of infrastructure development has to be revisited and revitalized. Committee had put out a timely, practical, and balanced report on overhauling the PPP ecosystem.
Key recommendations of the committee–
- Contracts need to focus more on service delivery instead of fiscal benefits.
- Better identification and allocation of risks between stakeholders.
- Prudent utilization of viability gap funds where user charges cannot guarantee a robust revenue stream.
- Improved fiscal reporting practices and careful monitoring of performance.
- Report also included governance reform, institutional redesign, and capacity-building.
How government can redesign the PPP model?
- Redesign ecosystem–
- Overhaul the culture and attitude towards the conjoining of government entities and private partners for creating specific pieces of infrastructure.
- Plug and play– There needs to be an approach of give and take, instead of government interlocutors trying to adopt a purely transactional approach without adequate focus on outcomes.
- Minimizing risk– Passing on uncertain elements in a project like the land acquisition risk to the private partner.
- Incentives– The private partners also need to be incentivized to focus on project outcomes, with guard-rails in place to discourage rent-seeking behaviour.
- Regulatory front-
- Secure legislation– Promulgate a PPP legislation which can provide a robust legal ecosystem and procedural comfort to the various actors and stakeholders.
- Revenue flow assurance- The key to a successful PPP is to provide stable revenue flow assurances and a settled ecosystem to investors over long periods by means of policy stability, assurances possibly secured by law.
- Government partners in PPP arrangements need to ensure that open-ended arrangements that might entail unforeseeable risk are minimized for the private investor, including aspects such as land availability and community acceptance.
Way forward-
In a post COVID era, a focus area for public policy has to be the creation of a modern-day, sustainable and resilient infrastructure. Government needs to design a fresh approach and create a stable policy environment that provides comfort and incentives to private investors.